CIS 527
Lecture 9 - Networking Overview
7 Layer OSI Network Model
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport - TCP/UDP
- Network - IPv4/IPv6
- Data Link - Ethernet
- Physical - 100BASE-T
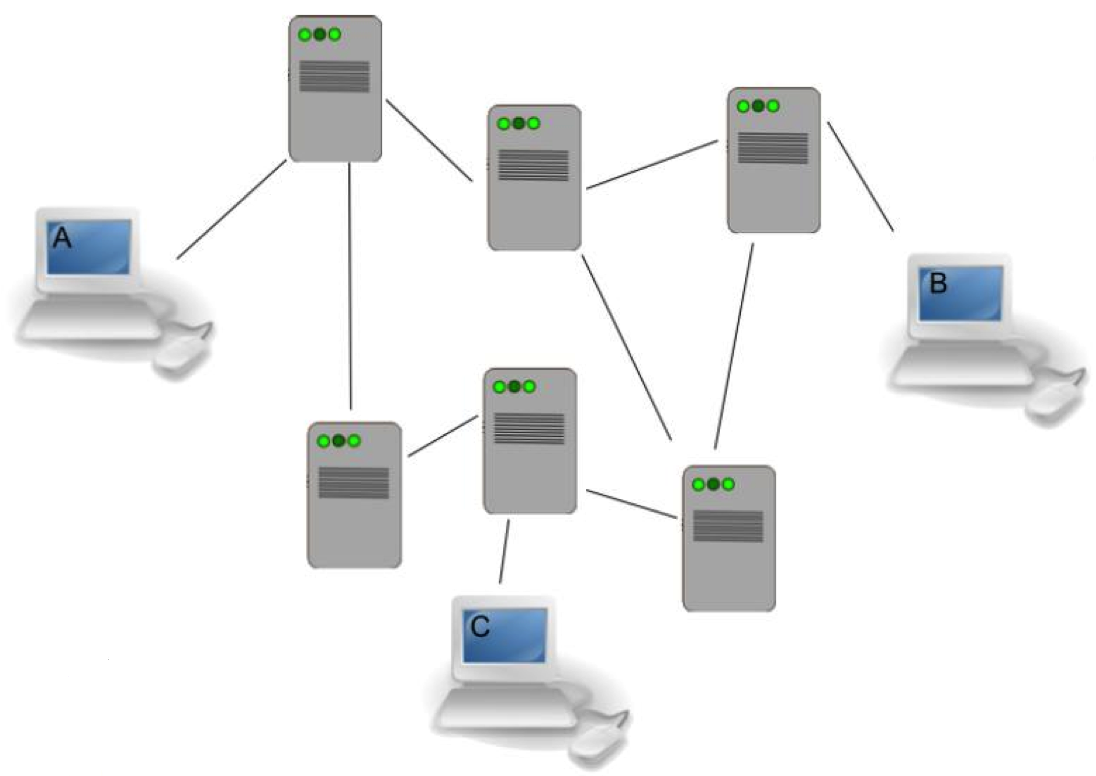
Routing
- Determines best way to get from point to point on a network
- Prevents loops
- Allows for redundant links in case of an error
- Simple networks use Spanning Tree Algorithm
Virtual LAN
- Partition a single layer-2 network
- Each partition is isolated
- Helps simplify network design
- Group items by function, not location
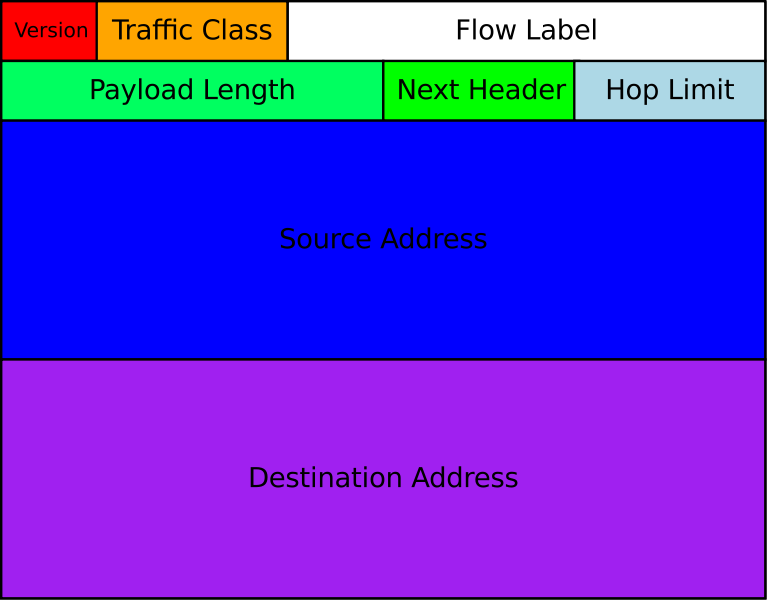
Network - IPv4
| IPv4 Packet Structure | |
| Version Info | Length |
| Packet ID | Flags & Offset |
| Protocol & TTL | Checksum |
| Source IP Address | |
| Destination IP Address | |
| Data... | |
IPv4 vs. IPv6
IPv4: 32 bit Addresses
232 = 4,294,967,296
IPv6: 128 bit Addresses
2128 = 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,
374,607,431,768,211,456
or 340 Undecillion addresses
Network Interfaces
- Localhost
- Ethernet Adapter
- Wireless Adapter
Localhost
- a.k.a Loopback Adapter (lo)
- IP Address: 127.0.0.1
- DNS Name: localhost
- Defined in Software
- Allows a system to access itself via nework protocols
Network Adapters
- Physical hardware connections to a network
- Includes Wired (Ethernet) and Wireless adapters
- Each adapter may have 1 or more IP addresses
Windows Network Adapters
Device Manager
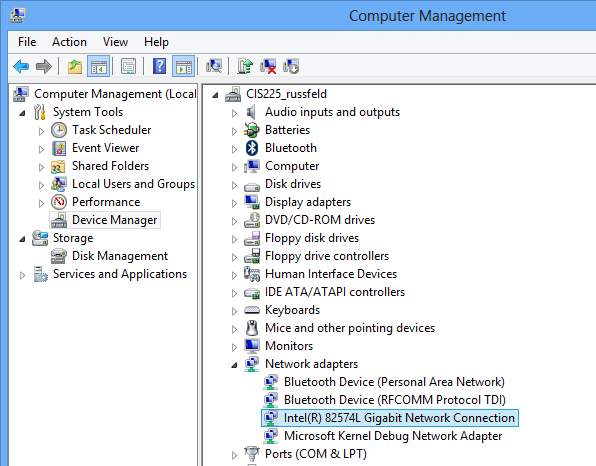
Windows Network Adapters
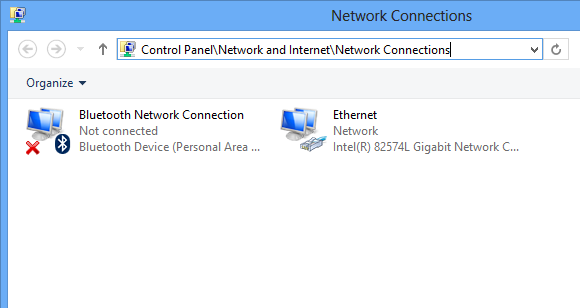
Network Connections
Ubuntu Network Adapters
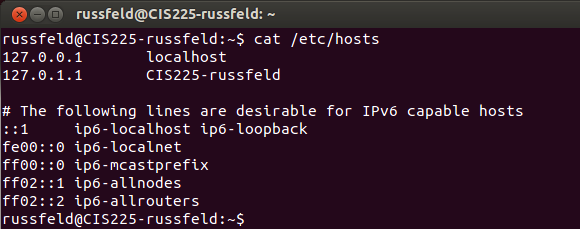
/etc/hosts
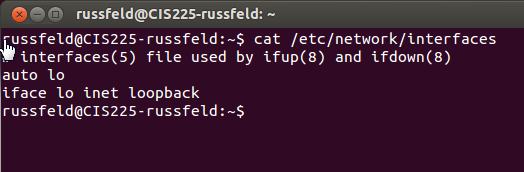
/etc/network/interfaces
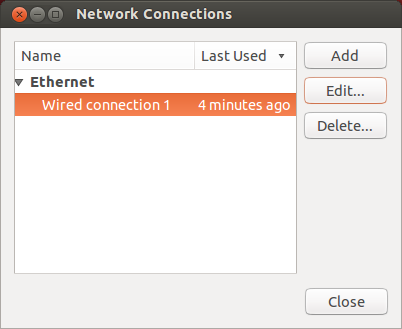
Ubuntu Network Adapters
IP Addresses
- Unique Identifier on a Network
- Used for packet routing
- 3 common configurations
- Automatic - DHCP
- Manual - Static IP Addresses
- Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
IP Address Components
- IP Address - The identifier of this computer
- Subnet Mask - The subnet this computer belongs to
- Default Gateway - The IP address of the "way out"
Subnet
- Logical subdivision of an IP network
- Aids in routing and management
- Traffic between subnets is exchanged across routers
Classess Inter-Domain Routing
- Early internet routing assigned 4 classes of networks
- A - 224 (16M) addresses
- B - 216 (65K) addresses
- C - 28 (256) addresses
- D - multicast addresses
- Inefficient usage of IP addresses
Subnet Mask
IP Address: 192.168.5.130
11000000.10101000.00000101.10000010
Subnet Mask
IP Address: 192.168.5.130
11000000.10101000.00000101.10000010
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Subnet Mask
IP Address: 192.168.5.130
11000000.10101000.00000101.10000010
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Network Prefix: 192.168.5.0
11000000.10101000.00000101.00000000
Subnet Mask
IP Address: 192.168.5.130
11000000.10101000.00000101.10000010
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Network Prefix: 192.168.5.0
11000000.10101000.00000101.00000000
Host Part: 0.0.0.130
00000000.00000000.00000000.10000010
CIDR Notation
- Number of bits in network prefix
- /8 = Class A size
- /16 = Class B size
- /24 = 255.255.255.0 = 254 hosts
- /26 = 255.255.255.192 = 62 hosts
- /28 = 255.255.255.240 = 14 hosts
- 192.168.5.0/24
Reserved IP Address Sections
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 169.254.0.0/16(APIPA)
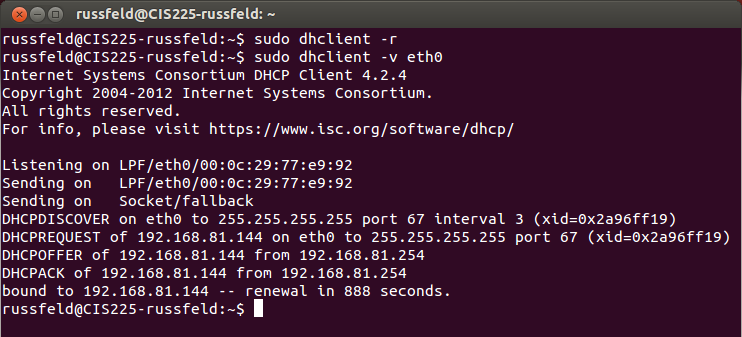
Ubuntu - dhclient
Manual Configuration
- Manually enter IP address information for hosts
- Normally used on servers and core network devices
- More control, but more work to make changes
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
- When all else fails, your system will assign an address that is non-routable
- If your IP is like 169.254.x.x then something is not working correctly
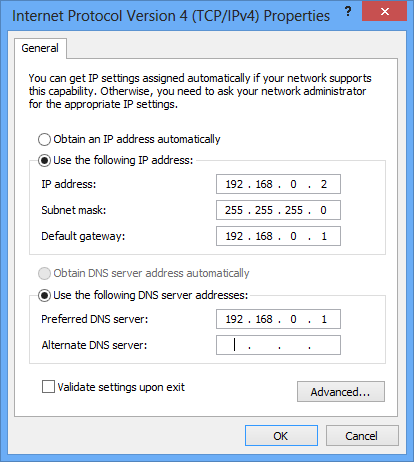
Windows IP Configuration
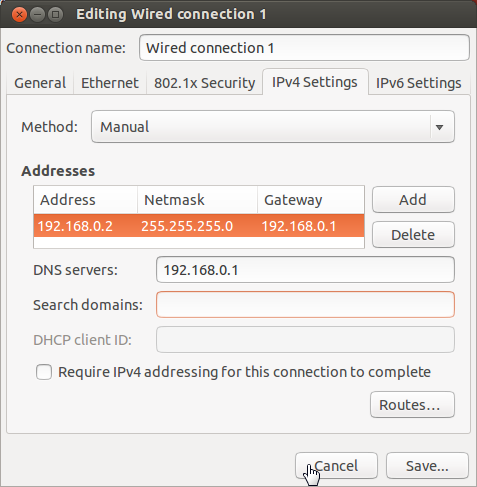
Ubuntu IP Configuration
Windows Diagnostic Commands
- ping - contact IP addresses and DNS names
- tracert - trace route between hosts
- ipconfig - access IP configuration
ipconfig
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
- ipconfig /all
- ipconfig /flushdns
- ipconfig /displaydns
Ubuntu Diagnostic Commands
- ping - contact IP addresses and DNS names
- traceroute - trace route between hosts
- ifconfig - access IP configuration
- mtr - combine ping and traceroute
Transport - TCP
| TCP Packet Structure | |
| Source Port | Dest. Port |
| Sequence Number | |
| Acknowledgement Number | |
| Options | Length |
| Checksum | Urgent |
| Data... | |
Transport - UDP
| UDP Packet Structure | |
| Source Port | Dest. Port |
| Length | Checksum |
| Data... | |
TCP vs. UDP
| TCP | UDP |
| Connection Oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliable | Unreliable |
| Acknowledge | No Acknowledge |
Ports
- Individual connection points for each application on a computer
- 65535 possible ports (216)
- Around 250 are "well known" ports with widely accepted uses for incoming connections
- Outgoing connections use high numbered "ephemeral" ports
Well Known Ports
/etc/services
- 21 - FTP
- 22 - SSH
- 25 - SMTP
- 80 - HTTP
- 443 - HTTPS
- 3389 - Remote Desktop
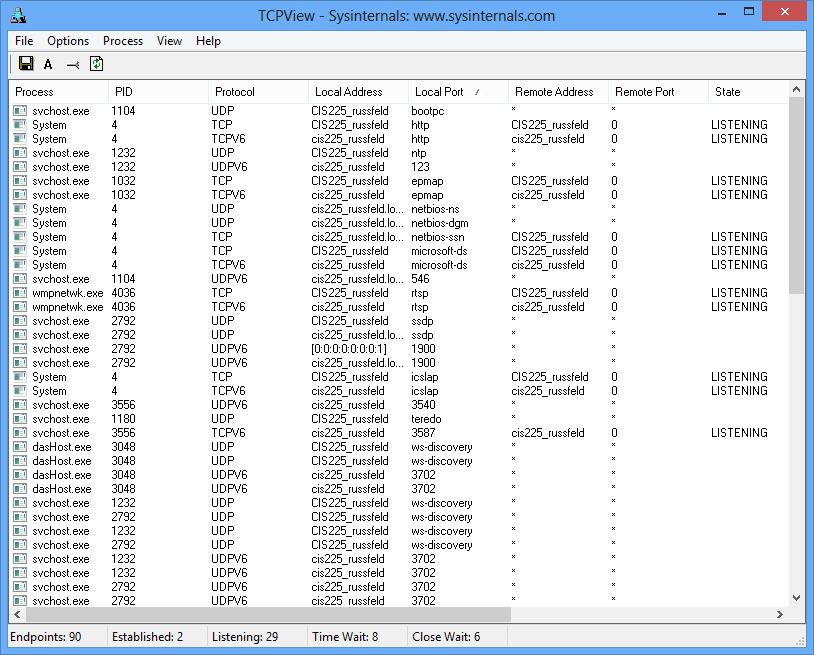
Windows - Sysinternals TCPView
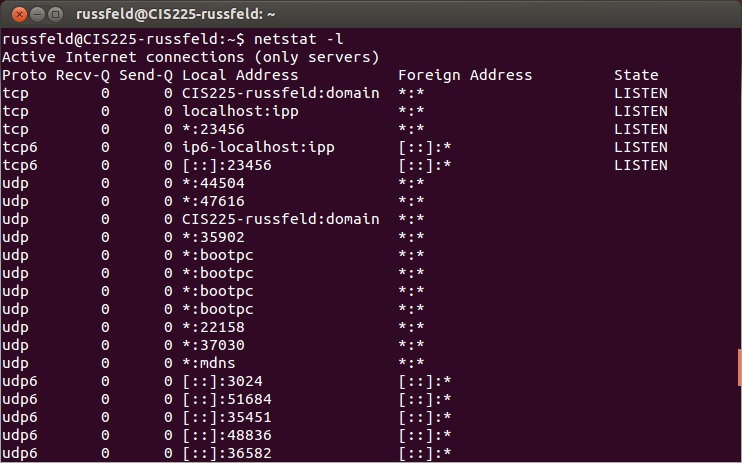
Ubuntu - netstat
Assignments
- Lab Help Session Fridays 9 - 10 AM!
- Lab 3 - Networking Services - Due Sunday, Mar 9th by 11:59 PM
- Set up Core Network Services & Network Monitoring
- Turn in:
- CIS Transient Storage
- via Storage Media in class Monday Mar 9th