CIS 225
Networking
7 Layer OSI Network Model
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport - TCP/UDP
- Network - IPv4/IPv6
- Data Link - Ethernet
- Physical - 100BASE-T
Network - IPv4
| IPv4 Packet Structure | |
| Version Info | Length |
| Packet ID | Flags & Offset |
| Protocol & TTL | Checksum |
| Source IP Address | |
| Destination IP Address | |
| Data... | |
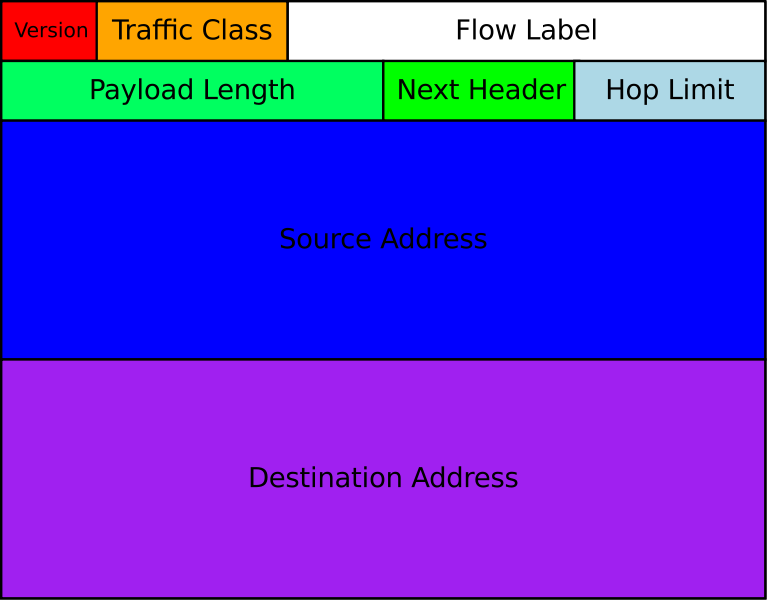
IPv4 vs. IPv6
IPv4: 32 bit Addresses
232 = 4,294,967,296
IPv6: 128 bit Addresses
2128 = 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,
374,607,431,768,211,456
or 340 Undecillion addresses
Network Interfaces
- Localhost
- Ethernet Adapter
- Wireless Adapter
Localhost
- a.k.a Loopback Adapter (lo)
- IP Address: 127.0.0.1
- DNS Name: localhost
- Defined in Software
- Allows a system to access itself via nework protocols
Network Adapters
- Physical hardware connections to a network
- Includes Wired (Ethernet) and Wireless adapters
- Each adapter may have 1 or more IP addresses
Windows Network Adapters
Device Manager
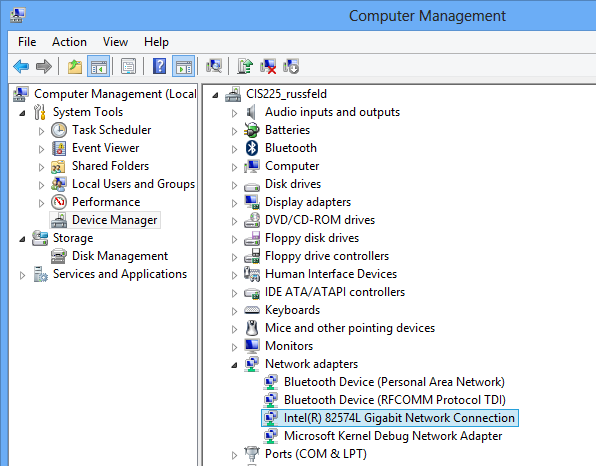
Windows Network Adapters
Network Connections
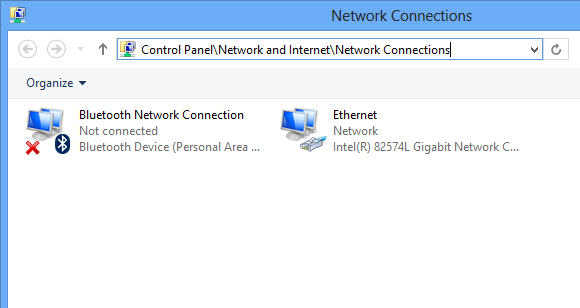
Ubuntu Network Adapters
/etc/hosts
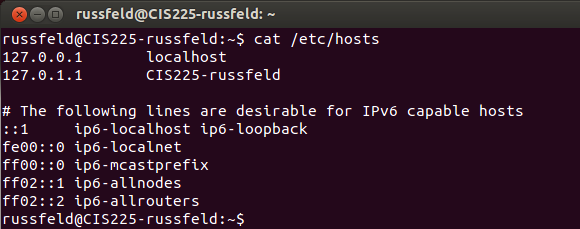
/etc/network/interfaces
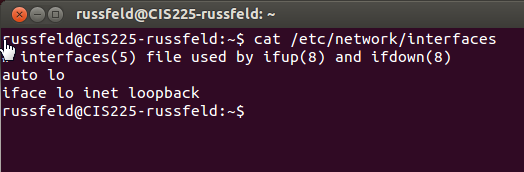
Ubuntu Network Adapters
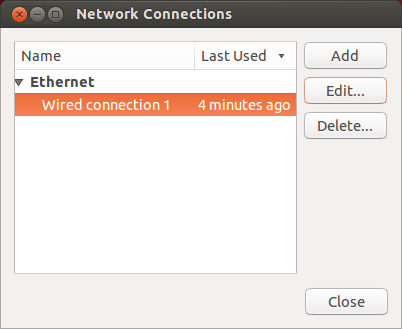
IP Addresses
- Unique Identifier on a Network
- Used for packet routing
- 3 common configurations
- Automatic - DHCP
- Manual - Static IP Addresses
- Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
IP Address Components
- IP Address - The identifier of this computer
- Subnet Mask - The subnet this computer belongs to
- Default Gateway - The IP address of the "way out"
Reserved IP Address Sections
- 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.254 (255.255.0.0)
- 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.254 (255.240.0.0)
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.254 (255.0.0.0)
- 169.254.0.0 - 169.254.255.254 (APIPA)
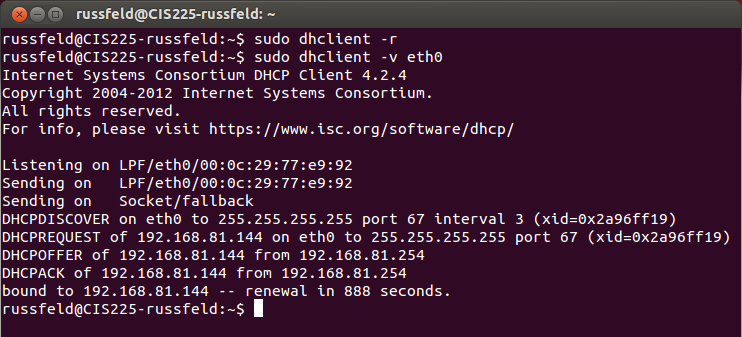
Ubuntu - dhclient
Manual Configuration
- Manually enter IP address information for hosts
- Normally used on servers and core network devices
- More control, but more work to make changes
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
- When all else fails, your system will assign an address that is non-routable
- If your IP is like 169.254.x.x then something is not working correctly
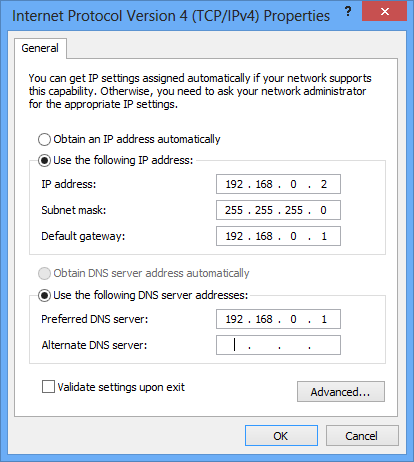
Windows IP Configuration
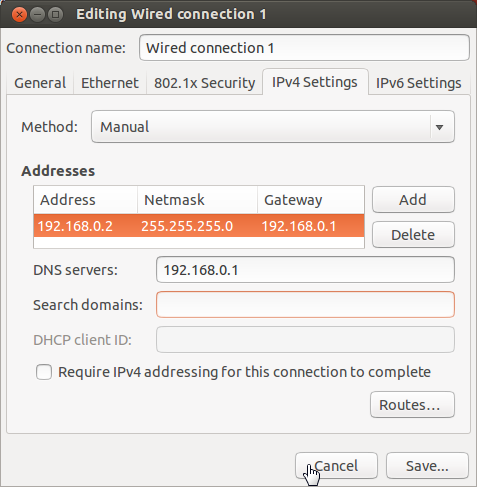
Ubuntu IP Configuration
Windows Diagnostic Commands
- ping - contact IP addresses and DNS names
- tracert - trace route between hosts
- ipconfig - access IP configuration
ipconfig
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
- ipconfig /all
- ipconfig /flushdns
- ipconfig /displaydns
Ubuntu Diagnostic Commands
- ping - contact IP addresses and DNS names
- traceroute - trace route between hosts
- ifconfig - access IP configuration
- mtr - combine ping and traceroute
Transport - TCP
| TCP Packet Structure | |
| Source Port | Dest. Port |
| Sequence Number | |
| Acknowledgement Number | |
| Options | Length |
| Checksum | Urgent |
| Data... | |
Transport - UDP
| UDP Packet Structure | |
| Source Port | Dest. Port |
| Length | Checksum |
| Data... | |
TCP vs. UDP
| TCP | UDP |
| Connection Oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliable | Unreliable |
| Acknowledge | No Acknowledge |
Ports
- Individual connection points for each application on a computer
- 65535 possible ports (216)
- Around 250 are "well known" ports with widely accepted uses for incoming connections
- Outgoing connections use high numbered "ephemeral" ports
Well Known Ports
/etc/services
- 21 - FTP
- 22 - SSH
- 25 - SMTP
- 80 - HTTP
- 443 - HTTPS
- 3389 - Remote Desktop
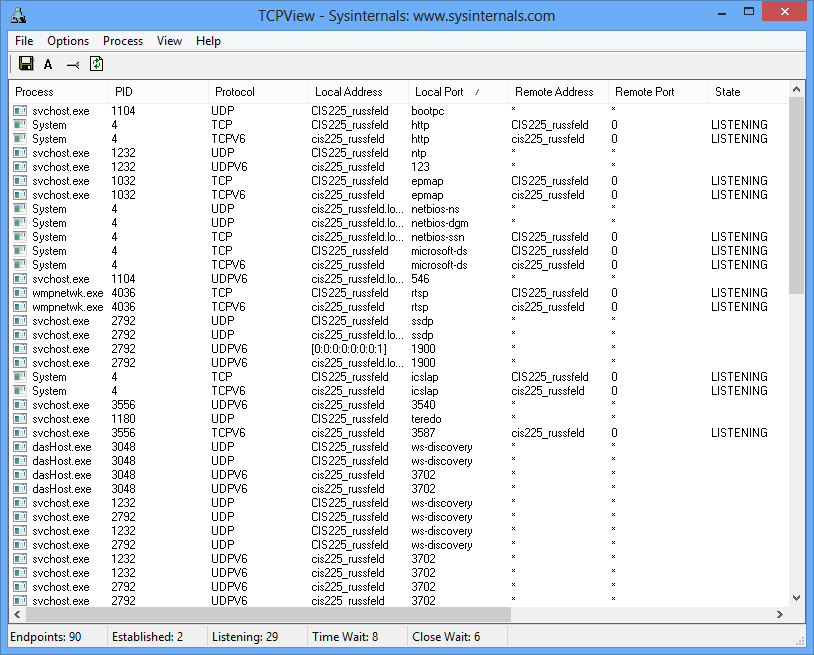
Windows - Sysinternals TCPView
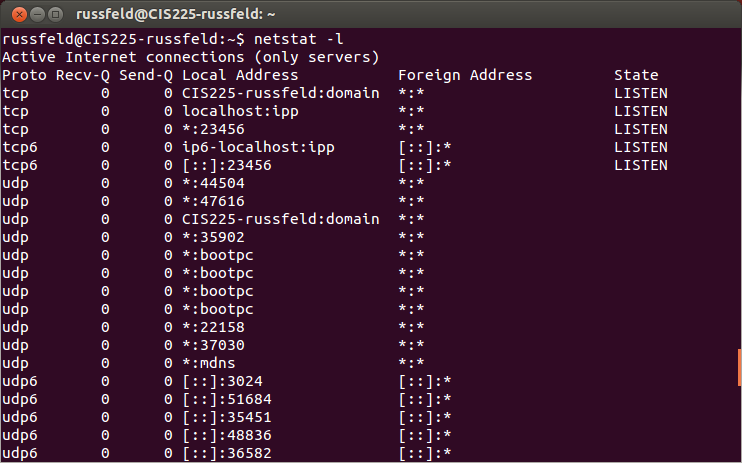
Ubuntu - netstat
Sharing
- Accessing files from one computer on another
- Building block of small networks
- Can also share printers, internet connections
Windows Sharing
- Uses Server Message Block (SMB) Application Layer Protocol
- Based on the Common Internet File System (CIFS)
- Uses ports 137-139, 445
Ubuntu Sharing
- Samba package enables Ubuntu to communicate using SMB
- Ubuntu can then share files with Windows and vice-versa
Network Security
- Authentication & Authorization
- Intrusion Detection System
- Encryption
- Honeypots
- Log Monitoring
- NAT Routing
- Firewalls
Authentication & Authorization
- Verify that users or devices on the network are valid
- Confirm that users are allowed to access resources
- Enforced with ACLs, firewalls, etc.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
- Monitors network activity
- Uses signatures or statistical anomalies to detect unwanted network activity
- Can be programmed to automatically respond to detected threats
Encryption
- Protect network traffic by encrypting it
- Prevents eavesdroppers from listening in and intercepting data
Honeypots
- Fake network resources left open
- Any attempts to access are assumed to be malicious
- Information gained is used to strengthen protection
Log Monitoring
- Many network enabled programs are configured to log connections
- Those logs can be analyzed to find unwanted connections
NAT Routing
- Network Address Translation
- Multiple devices with different internal IP addresses share one public IP address
- External attackers only see router (unless ports are forwarded)
- Protects internal systems by not making them directly accessible externally
Firewalls
- Restrict network access to specific programs, ports, addresses, protocols, etc.
- Can be employed on an entire network or each individual system (or both)
Firewalls vs IDS
- Firewalls look at types of traffic, IDS looks at contents and meaning of traffic
- Firewalls can only prevent unwanted connections, IDS can detect them already in progress
Lab 5
- Confirm you can ping back and forth
- Set up sharing to and from each virtual machine
- Turn on Firewalls
- Create Firewall Rules to allow access to the following resources
- Remote Connection (SSH/RDP)
- Shared Files (smb/Samba)
- Web Server (apache/IIS)
Reading
Assignments
- Lab 5 - Networking
Due 10/10 12:30 PM