CIS 225
User Account Management
User Accounts
- Allows multiple people to share resources
- Each user can have different permissions
- Aids in auditing (who did what)
- Protects system from unauthorized use
Authentication vs. Authorization
- Authentication - Confirming a user is who he or she claims to be (logging in)
- Authorization - Allow an authenticated user access to specific resources
- Authentication DOES NOT IMPLY Authorization
Authentication Methods
One or more of the following factors
- Ownership factors - something user has
- Knowledge factors - something user knows
- Inherence factors - something user is or does
Authorization Methods
- Security Policies
- Access Control Lists (ACL)
- File System Security Settings
User Identification
- Operating systems refer to users by a unique identifier
- Linux: user identifier (UID)
- Windows: security identifier (SID)
- This allows user to change usernames without affecting the account
User Account Information
- UID / SID
- Username
- Password
- Home directory
- Group(s)
Groups
- List of user accounts
- Aid in assigning access to users
- Each user may be a part of one or many groups
- Unique identifier
- Linux: group identifier (GID)
- Windows: security identifier (SID)
Windows 10 - Settings
Windows 10 - Control Panel
Windows 10 - Management
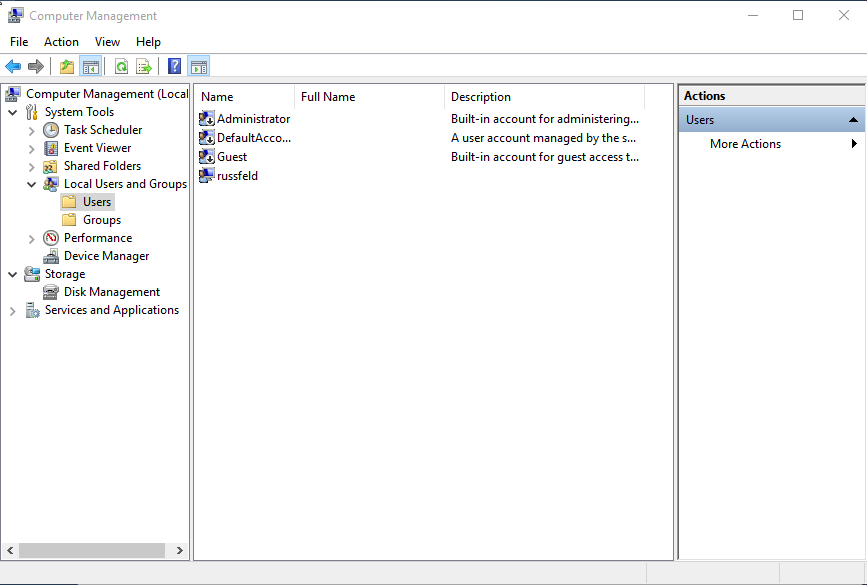
Windows 10 Default Accounts
- Administrator
- Access to everything
- Cannot be deleted
- Disabled by default
- Has no password by default
- Guest
- Limited access
- Disabled by default
Windows 10 Pseudo Accounts
- LocalSystem - system-level tasks & services
- LocalService - fewer rights than LocalSystem
- NetworkService - fewer rights than LocalService, but allows network access
Windows 10 Default Groups
- Administrators - complete access
- Event Log Readers - read event logs
- Guests - access system only
- Power Users - not used
- Remote Desktop Users - log on remotely
- Users - normal users
Many others, refer to documentation
User Account Control
- Protects the system from unwanted changes
- Allows administrators to run commands from a non-administrator account
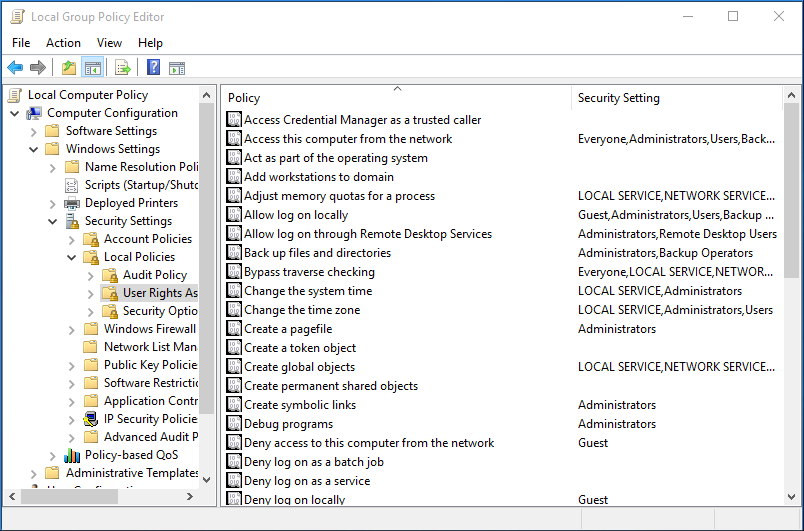
Local Group Policy Editor
WIN+R - gpedit.msc
Ubuntu Account Types
- Super User (root)
- Complete control of the system
- Disabled by default on Ubuntu
- UID = 0; GID = 0
- Regular User
- User who can log on to the system
- System User
- Used by programs and services to interact with the system
Ubuntu Accounts
Regular Users:
- UID: starting at 1000 and up
- Each account has a private group created with matching GID and is made a member of that group
- Each account receives a skeleton directory in /home
Ubuntu Accounts - System Settings
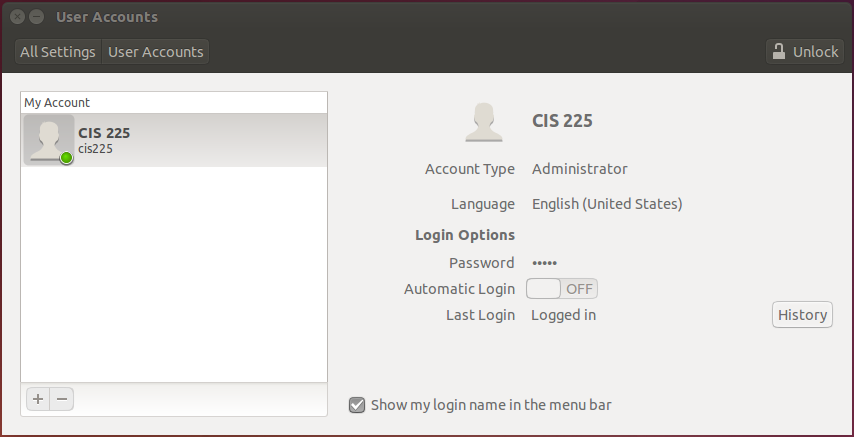
Ubuntu Accounts - Users & Groups
Install "gnome-system-tools"
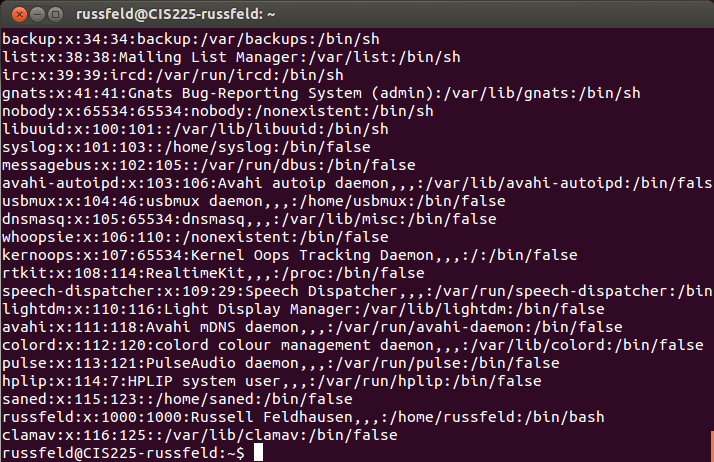
/etc/passwd
/etc/shadow
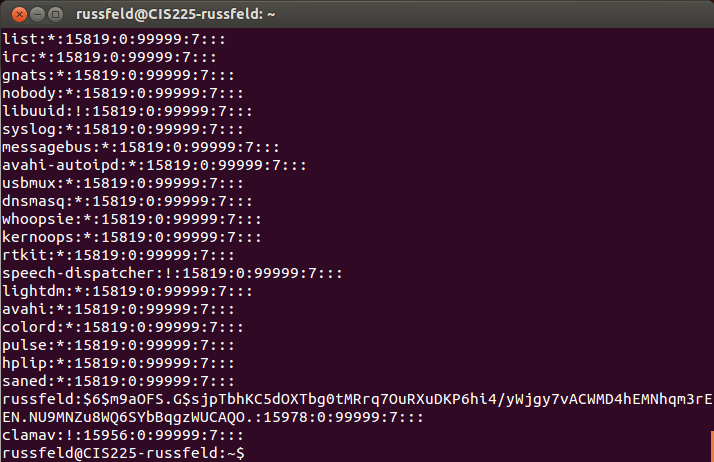
/etc/group
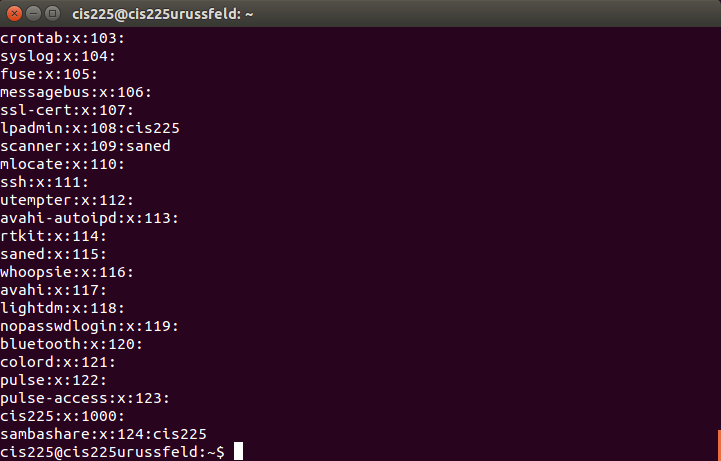
Commands
- groupadd - add a group
- groupdel - remove a group
- groupmod - modify group
- gpasswd - change group administrator or password
- useradd - add a system user
- userdel - remove a user
- usermod - modify a user
- adduser - add a regular user
- passwd - change password
sudo
- Short for "super user do"
- Allows regular users to run commands as root user
- User and rights listed in /etc/sudoers
- Add users to the "sudo" or "admin" group to give them access
- Use 'visudo' command to edit file
Best Practices
- Each person must have a unique account
- Enforce strong passwords & regular changes
- Assign minimal rights by default
- Log any logins/logouts/sudo usage
- Remove unneeded users ASAP
- Don't use admin account for daily use
Reading
Assignments
- Lab 2 - Virtualization, OS Install & Config
Due 9/16 11:30 AM Before Lecture!! - Lab 3 - User Accounts & File Systems
Due 9/28 11:30 AM Before Lecture!!