CIS 225
Lecture 21 - Backup Strategies
Backup Strategies
- Who
- What
- When
- Where
- Why
- How
Backup Strategies
- Who owns the data
- What data must be stored
- When backups should be made
- Where backups should be stored
- Why data loss occurs
- How should it be created
Who Owns the Data
- Who has data that should be backed up?
- What data is needed to function?
- Do we have enough resources to back up data?
What data must be Stored
- Accounting Data
- Sales Records
- Inventory
- Health Records
- Personnel Records
- User Data & Files
When backups should be made
- Yearly
- Monthly
- Weekly
- Daily
- Hourly
- Instantly
Where backups should be stored
- Rotational Hard Disk
- Solid State Storage
- Optical Storage
- Magnetic Tape
- Cloud Storage
- Paper Storage
Where backups should be stored
- Rotational Hard Disk
- PRO: Cheap, fairly fast, common
- CON: Moving parts, not long-term
- Solid State Storage
- PRO: Fast, no moving parts
- CON: Expensive, long-term stability unknown
Where backups should be stored
- Optical Storage (CD/DVD)
- PRO: Cheap, easy to use
- CON: Small space, easily damaged
- Magnetic Tape
- PRO: High capacity, long-term
- CON: Expensive, slow, must rotate tapes
Where backups should be stored
- Cloud Storage
- PRO: Cost effective, offsite, large
- CON: No direct control, trust
- Paper Storage
- PRO: Lasts forever, secure from cyber attacks
- CON: Hard to verify/restore data, flammable
Where backups should be stored
- On-line - RAID, Network Drives, etc.
- Near-line - Tape Systems
- Off-line - Disconnected but nearby
- Off-site - Different location
- Backup Site (DR Center) - includes hardware ready to go
Source: Wikipedia
Why data loss occurs
- Accidental Deletion
- Software/Hardware Failures
- Data Corruption over Time
- Malicious Intent
- Natural Disasters
How should it be created?
- Unstructured
- Full Image
- Incremental
- Differential
- Reverse Delta
- Continuous
Source: Wikipedia
Unstructured
"Just a pile of CDs"
- PRO: Requires little training or software to accomplish
- CON: Depends on the user to perform backups; backups may be lost/damaged/unverified and not useful when needed
Full Image
Contains a complete copy of all files
- PRO: Each backup has everything; simple software can create the backups; can be used to create "known good" states
- CON: Large amounts of storage needed; hard to see multiple versions of files
Incremental
Only store changes since last full/incremental backup
- PRO: Efficient use of storage; easy to see multiple versions
- CON: Requires complex software; loss of a any backup invalidates all later incrementals
Differential
Only store changes since last full backup
- PRO: Efficient use of storage; easy to see multiple versions
- CON: Requires complex software; loss of a full backup invalidates all differentials
Reverse Delta
Most recent backup is a full; all previous versions are based on most recent
- PRO: Efficient use of storage; easy to see multiple versions; most recent backup is readily available
- CON: Requires complex software; loss of a recent backup invalidates all backups
Comparison
| Day | Incremental | Differential |
| Sun | Full | Full |
| Mon | Since Sun | Since Sun |
| Tue | Since Mon | Since Sun |
| Wed | Since Tues | Since Sun |
| Thu | Since Wed | Since Sun |
| Fri | Since Thu | Since Sun |
| Sat | Since Fri | Since Sun |
Continuous
Instantly back-up any changes made
- PRO: Very little data loss;
- CON: Lots of storage; additional overhead on running systems
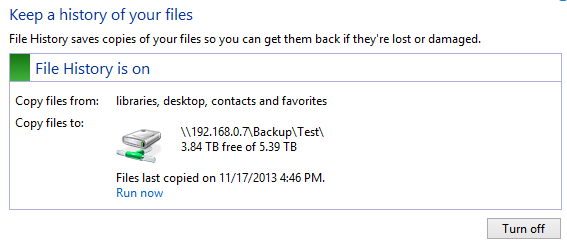
Windows File History
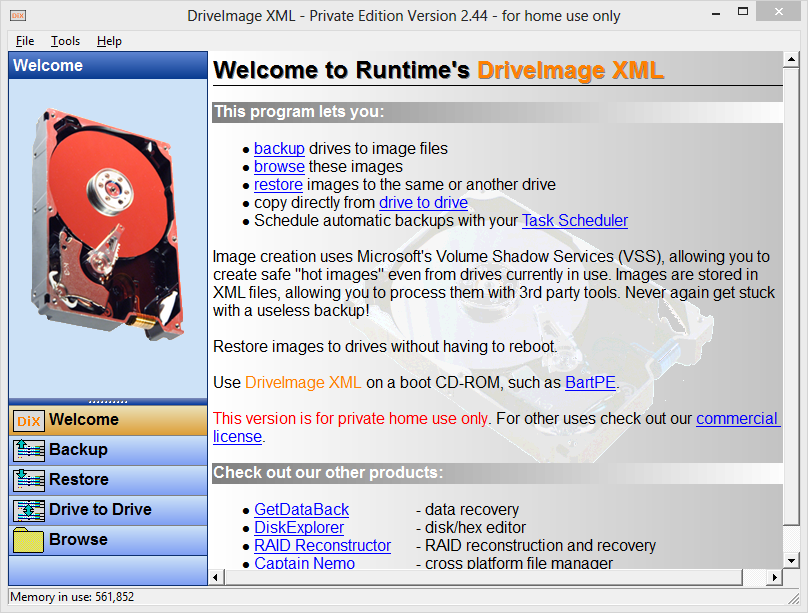
DriveImage XML
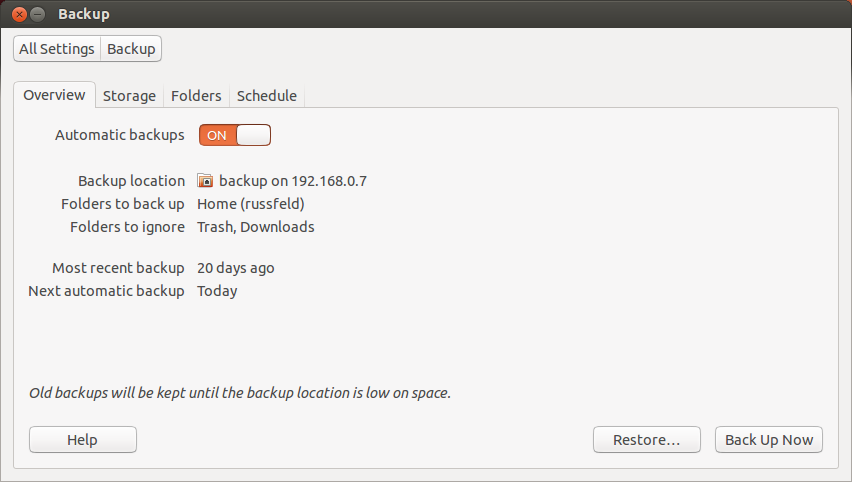
Ubuntu Deja-Dup
Assignments
- Lab 10 - Backups: Due 12/2 @ 11:59 PM
WARNING: A couple of steps may take 1 hour or more to run; allow plenty of time to complete this lab
