CIS 225
Lecture 14 - Software Architecture & Installation
Windows Software Architecture
- Executable Image (.EXE)
- Dynamic Link Library (.DLL)
- Initialization File (.INI)
- Registry Keys
- Drivers
- Services
Executable Image (.EXE)
- Contains the actual executable code for an application
- May also contain resources, graphics, fonts, etc.
- Based on the old Unix COFF (Common Object File Format)
Dynamic Link Library (.DLL)
- Shared library files used by programs
- Uses same format as .EXE file
- Programs can access same .DLL files simultaneously
Initialization File (.INI)
- Informal standard for configuration files
- Used extensively in Windows up to Windows ME for system & software settings
- Structured text files
Registry Keys
- Structured data storage for system settings
- Key <-> Value pairs
- Faster loading of settings
- Allows multiple users to use a system simultaneously
Windows Software Install Process
- Extract/expand files
- Place files in location
- Create registry keys
- Install drivers/services
- Create user data files
- Create shortcuts
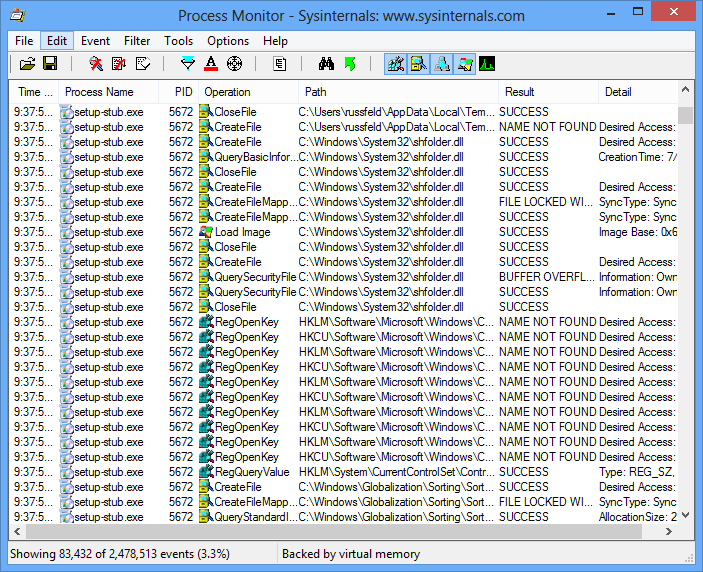
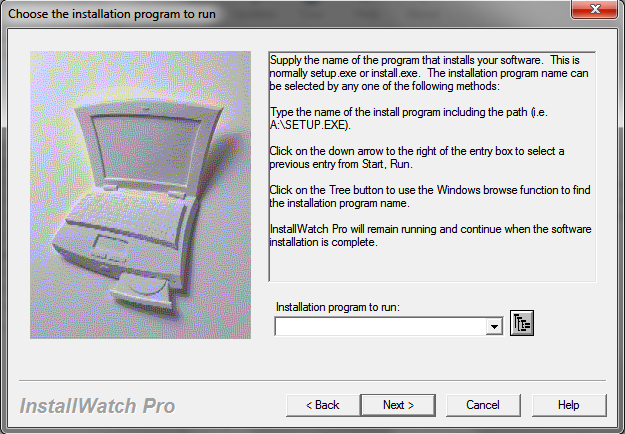
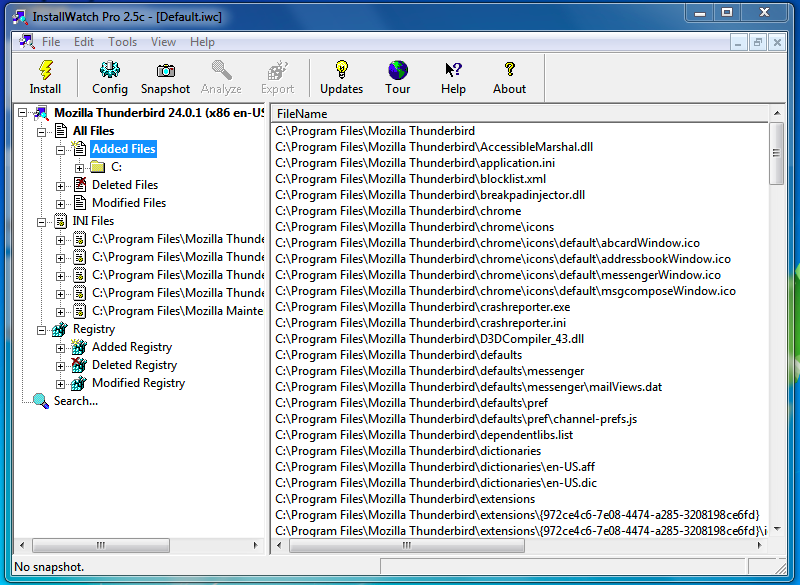
Installing - Thunderbird
Ubuntu Software Architecture
- Binary Files
- Shared Object Files (.SO)
- Library Files
- Settings Files
- Documentation Files
- Upstart/init scripts
Binary Files
- Contains the executable code for the application
- Uses the ELF (Executable and Linkable Format)
- Commonly used in many Unix-like systems
- Usually stored in /bin folder
Shared Object & Library Files
- Shared information or code used by multiple programs
- Install once, use everywhere
- May have to store multiple versions for different programs
- Usually stored in /usr/lib
Settings Files
- Configuration files used by programs
- Text based, similar to .INI files
- Usually stored in /etc for system-wide settings or in a hidden folder in ~/ (like ~/.thunderbird)
Documentation Files
- Stores information about the software
- Responds to 'man' command on terminal
- Usually stored in /usr/share folder
Ubuntu Package Management
- Most software installed via "packages"
- Packages are provided from a repository
- Programs such as Synaptic or apt can install packages
- Programs can also be installed from source
Ubuntu Software Install Process
- Extract/expand files
- Place files in location
- Create user data files (usually on first run)
- Create startup scripts
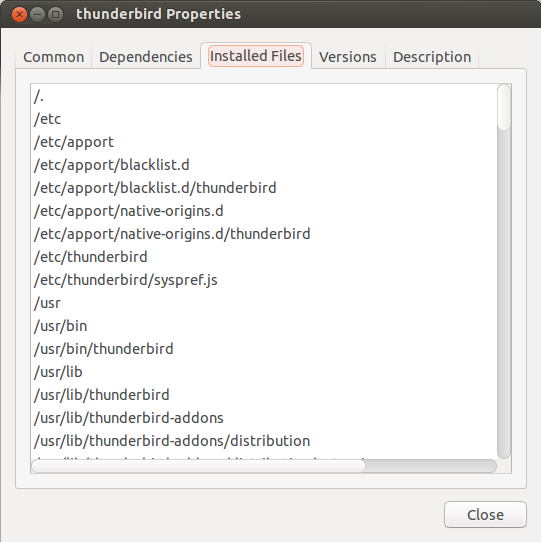
Tracking - Synaptic
Reading
- Ubuntu Unleashed - Chapter 22
Assignments
- Lab 6 - Service & Process Management and Software Install: Due 10/21 @ 11:59 PM