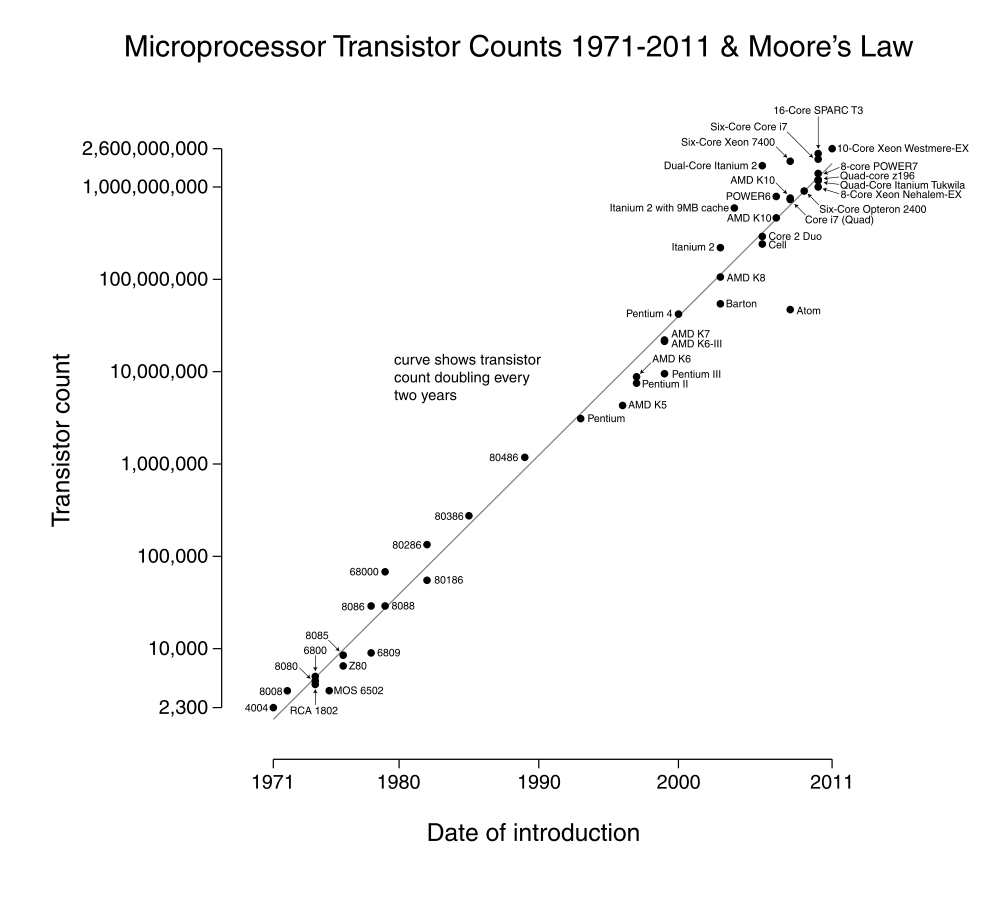
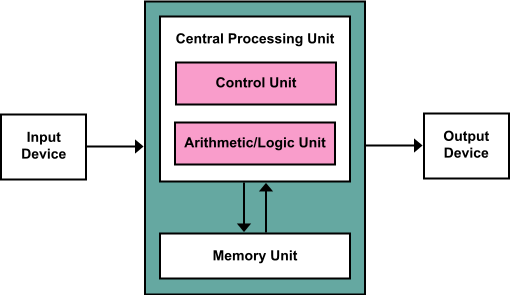
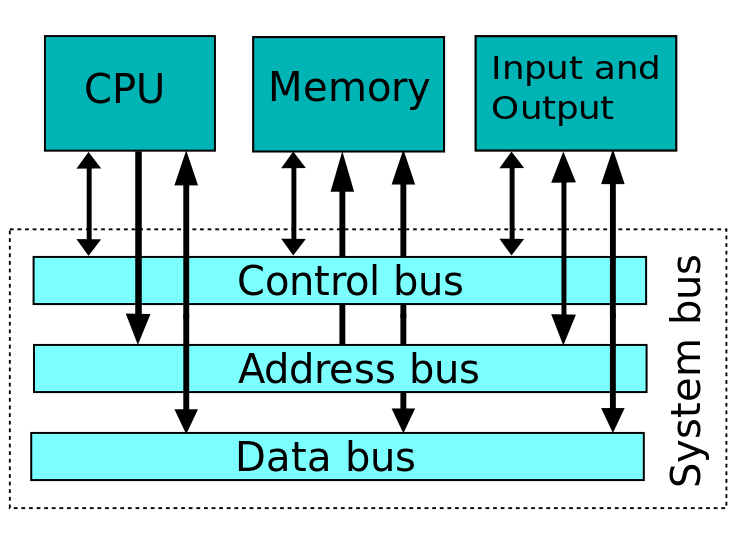
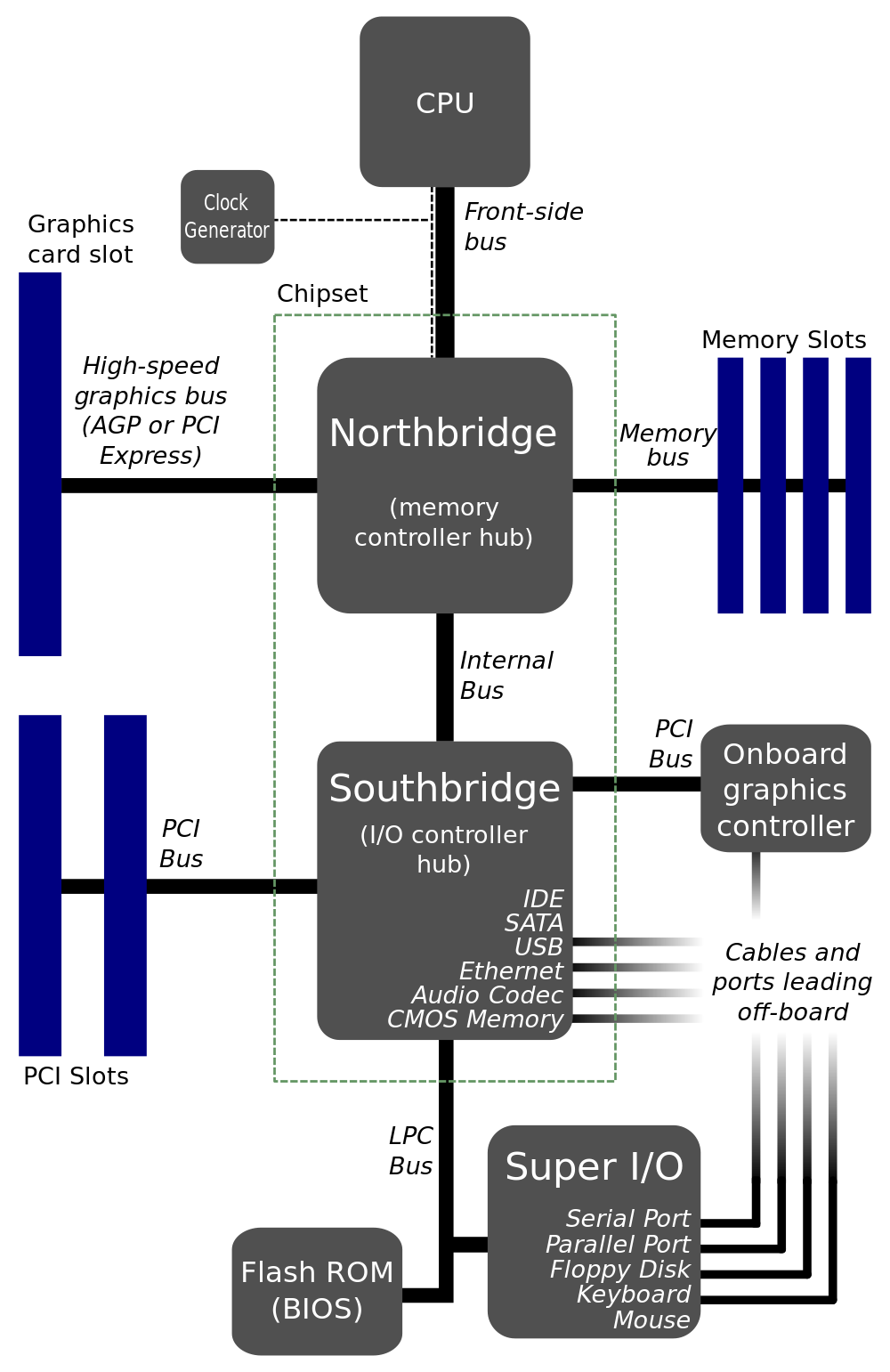
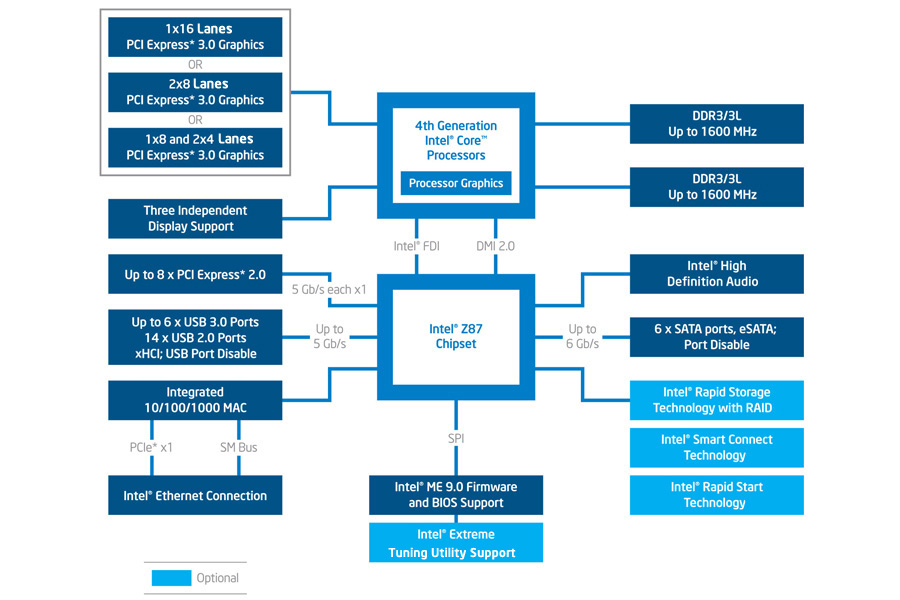
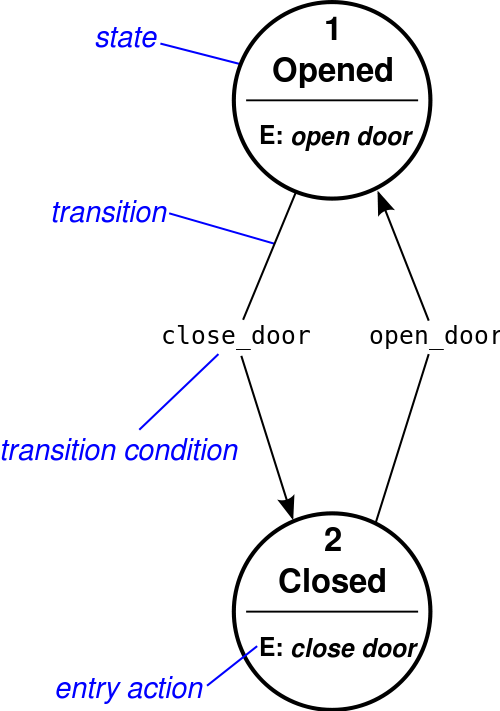
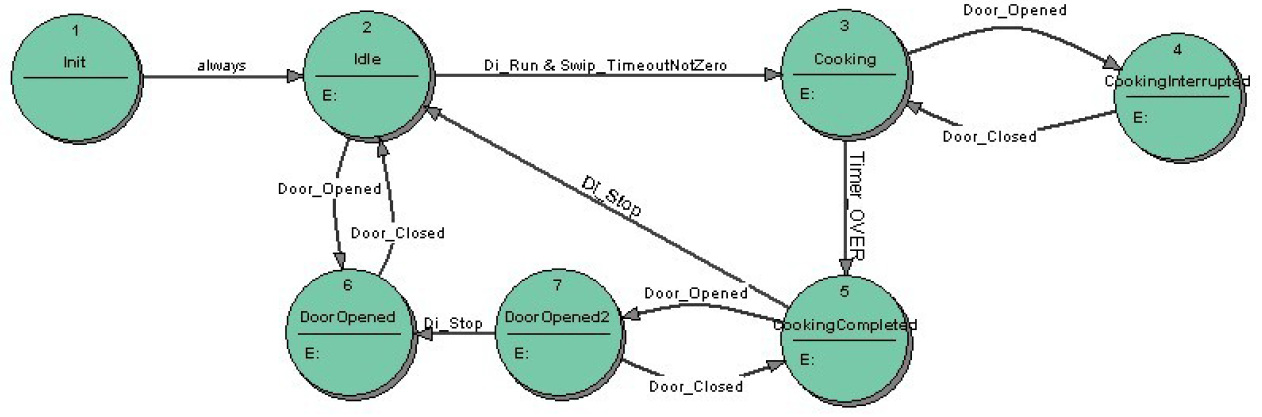
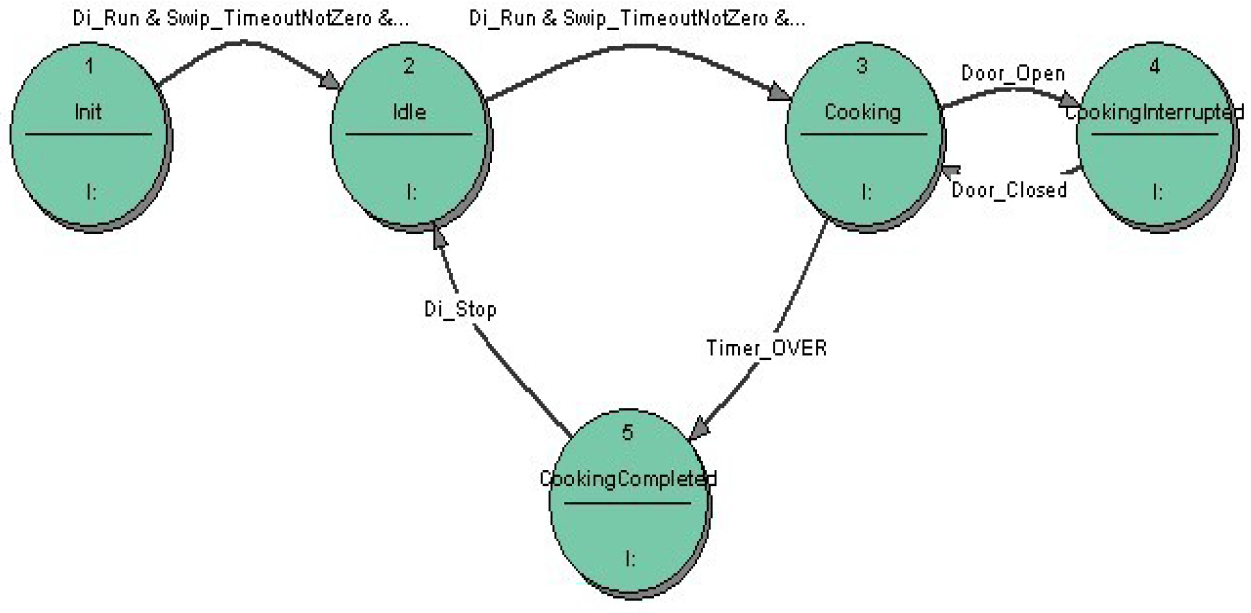
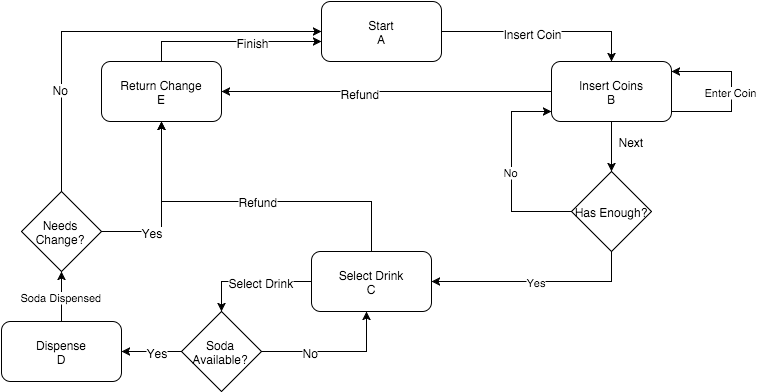
Blog 3: Making Meaning: POTS
Now that we’ve finished reading the first textbook, it is time to step back and think about what we read. Write about your reactions to it and what you learned from it. I’d recommend almost treating this like an in-depth book review for others who are interested in reading the book, but don’t mind some spoilers. Some questions I’d like you to answer:
- How did you feel reading this book? Engaged? Bored? Interested?
- What was the most interesting thing you learned?
- Were there any parts of the book you didn’t like?
- Were there any terms or concepts that you looked up (Googled) to find more information about? What were they? What did you find?
- Did this book help explain things you didn’t know about computers?
- Did this book leave you with any questions unanswered?
- Would you recommend this book to a friend that wanted to know more about computers?