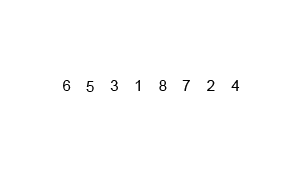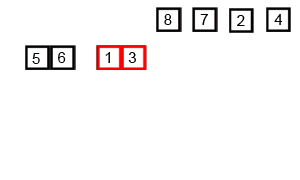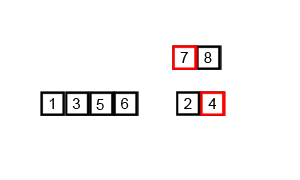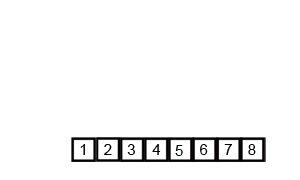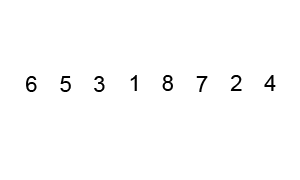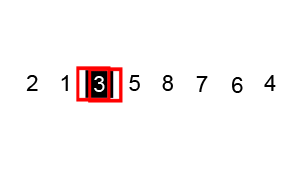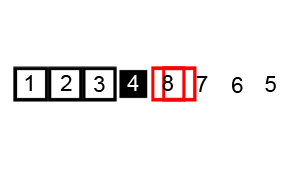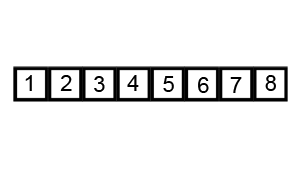CIS 115
Lecture 7: Algorithms
How do you shuffle cards?
- What items do you need?
- What tools do you need?
- What skills do you need?
- What prior knowledge do you need?
Algorithm
A finite list of specific instructions for carrying out a procedure or solving a problem
Euclid's Algorithm (GCD)
- Start with 2 numbers, A and B
- If either one is zero, the answer is the other number
- Subtract the smaller number from the larger number
- Repeat steps 2 - 4 until an answer is found
Example: GCD of 1071 & 462
Example: GCD of 1071 & 462
- 1071, 462
- 609, 462
- 147, 462
- 147, 315
- 147, 168
- 147, 21
- 126, 21
- 105, 21
- 84, 21
- 63, 21
- 42, 21
- 21, 21
- 21, 0
- 21
Sorting Algorithms
- Insertion Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quicksort
Insertion Sort

Image Source: Wikipedia
- Choose an element from the source
- Place it in the correct place in the destination
- Repeat until source is emtpy
Bubble Sort
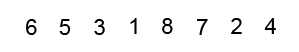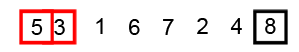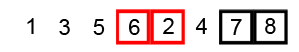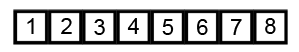
Image Source: Wikipedia
- Compare the first two elements
- If they are out order, swap them
- Move one element over and repeat
- When the end is reached, start over
- Continue until no more swaps are made
Big O Notation
- A way to express the complexity of an algorithm
- Approximates the number of steps needed based on the size of the input
- Assumes the input is a "worst case" input
Bubble Sort - Worst Case?
- 3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 6, 9, 8, J, 10, K, Q, A
- A, 2, K, 3, Q, 4, J, 5, 10, 6, 9, 7, 8
- A, Q, K, 10, J, 8, 9, 6, 7, 4, 5, 3, 2
- A, K, Q, J, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2
- 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, Q, A, 3, 5, 7, 9, J, K
Bubble Sort - Worst Case?
- 3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 6, 9, 8, J, 10, K, Q, A - 6
- A, 2, K, 3, Q, 4, J, 5, 10, 6, 9, 7, 8 - 42
- A, Q, K, 10, J, 8, 9, 6, 7, 4, 5, 3, 2 - 73
- A, K, Q, J, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2 - 78
- 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, Q, A, 3, 5, 7, 9, J, K - 21
Bubble Sort - Worst Case?
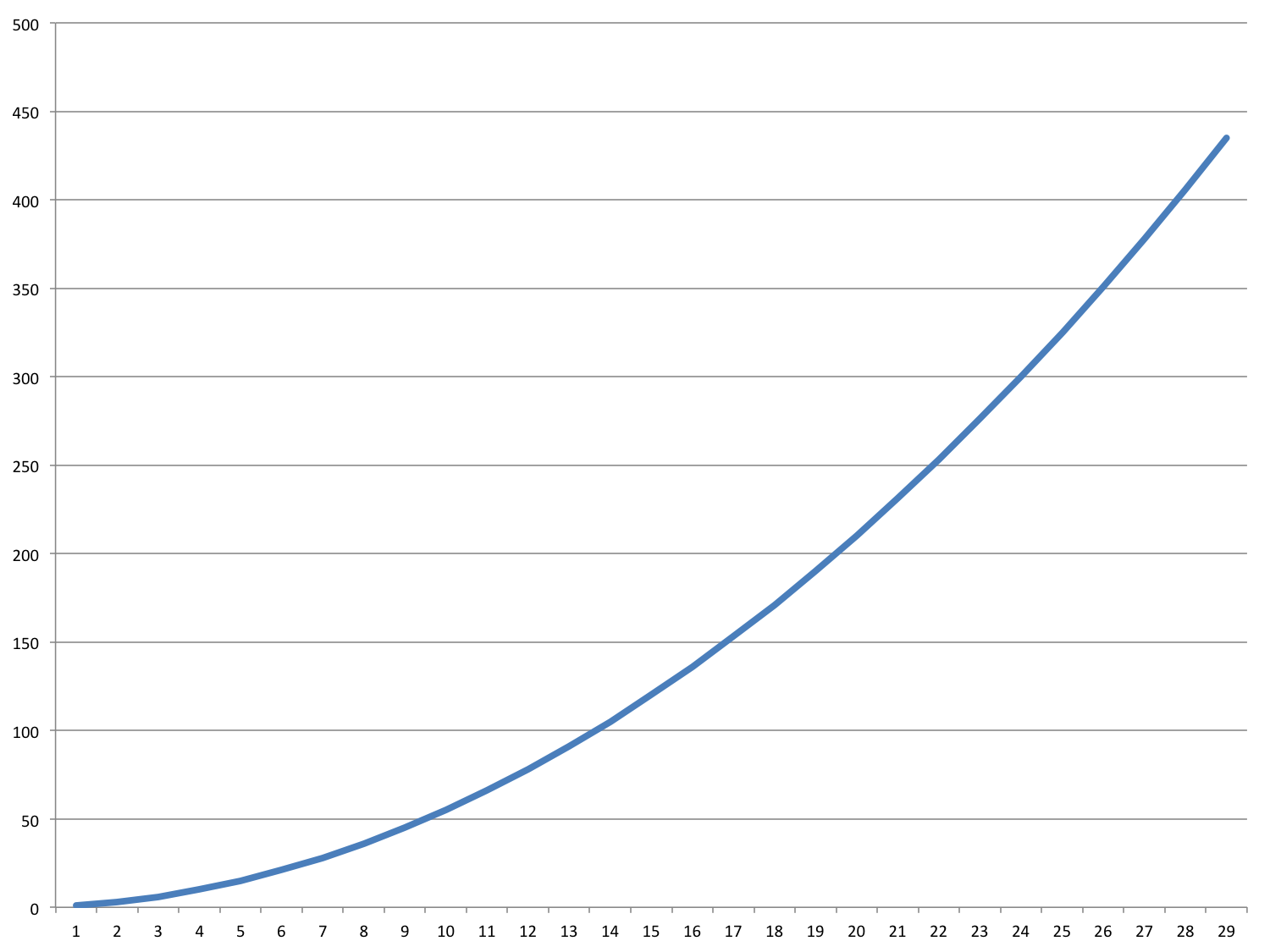
Sorting Algorithms
- Insertion Sort - O(n2)
- Bubble Sort - O(n2)
- Merge Sort
- Quicksort
Merge Sort
- Split the items into two halves
- Repeat step 1 until each has 1 item
- Choose 2 parts and merge them together by choosing the smallest item repeatedly from the front of each part
- Continue merging parts together until no more remain
Quicksort
- Choose an item from the list as a "pivot"
- Put all items less than that item to its left, and put all items greater to its right
- Repeat these steps for the items on each side of the pivot.
Sorting Algorithms
- Insertion Sort - O(n2)
- Bubble Sort - O(n2)
- Merge Sort - O(n log n)
- Quicksort - O(n2) - avg. O(n log n)
What is a Heuristic?
Using experience based techniques to find a satisfactory solution to a problem (which may or may not be the absolute best solution)
Everyday Heuristics
- Rule of Thumb
- Educated Guess
- Common Sense
- Try something and work backwards
- Do a simpler problem first
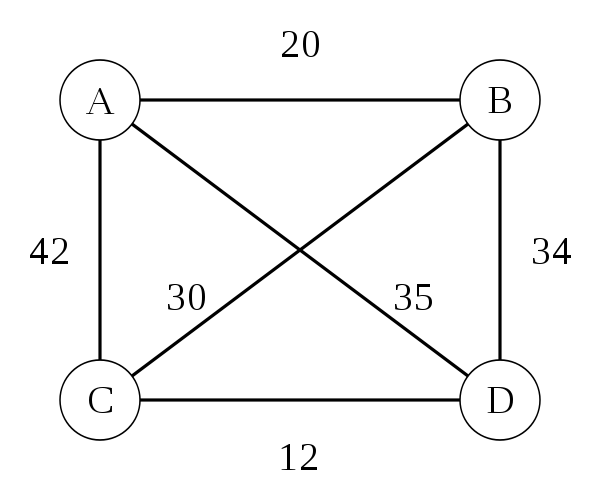
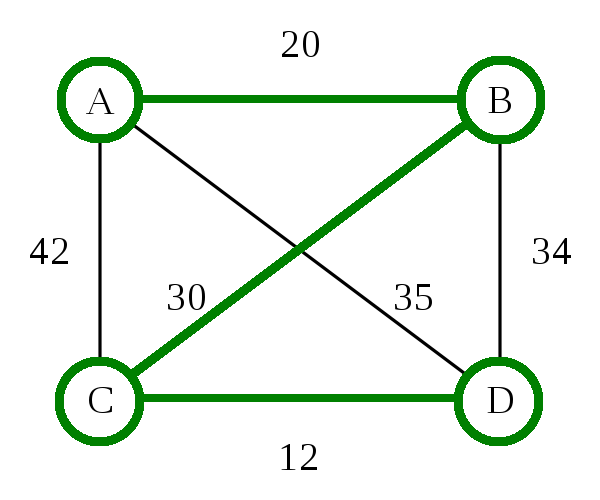
Travelling Salesman Problem: Algorithms
- Brute Force - O(n!)
- Easy & Cheap, but not fast
- 8 cities = 40320 steps
- Dynamic Programming - O(2n)
- Faster, but not easy or cheap
- 8 cities = 256 steps
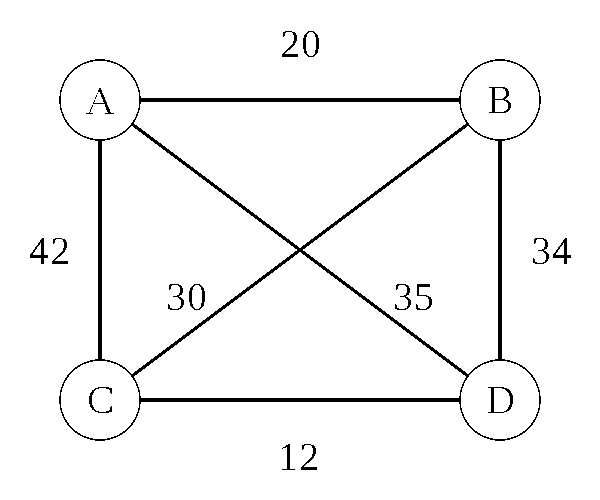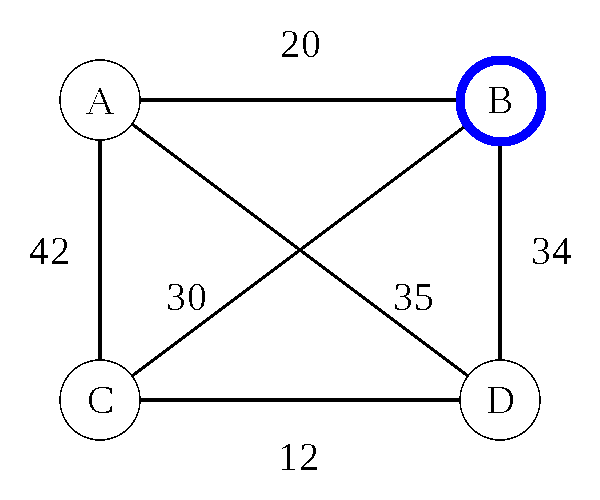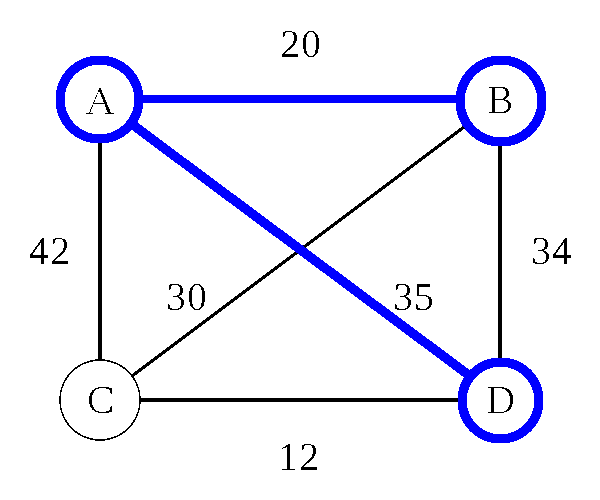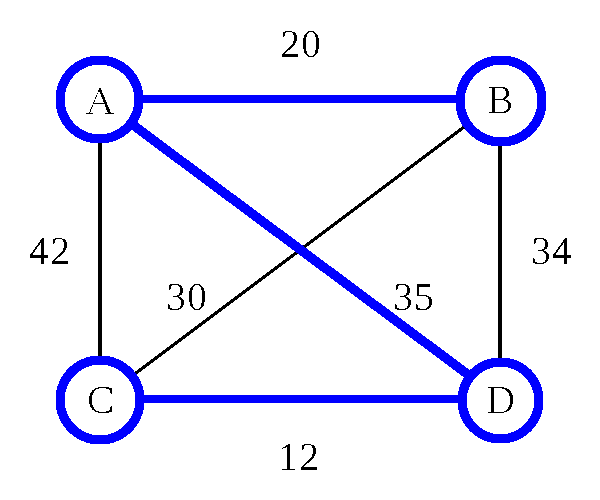
Travelling Salesman Problem: Heuristic
Nearest Neighbor (Greedy Algorithm)
- Pick any city (we'll use B)
- Go to the closest city you haven't been to yet
- From that city, repeat this process until all cities have been visited
Travelling Salesman Problem: Heuristic
Nearest Neighbor (Greedy Algorithm) - O(d n)
- d is the number of dimensions
- n is the number of cities
- 8 cities = 16 steps (assuming 2D maps)
Time can vary widely based on how the data is presented and sorted
Assignments
- Read and be prepared to discuss:
- Pattern on the Stone Chapter 6: Memory: Information and Secret Codes
- Blog 3: Algorithms -
Due 2/17 10:00 PM - Scratch Sorting Project -
Due 2/19 10:00 PM
Blog 3: Algorithms
Think about something that you do every day. That one thing probably is composed of many smaller steps, which you have to perform in the correct order. How would you describe those steps to someone unfamiliar with the action? How would you describe them to a robot that can follow your actions? While we may not think of it in this way very often, most of our daily lives could be expressed as an algorithm. Choose a few examples of actions you perform often, and write about how you would express them as algorithms. Some things to consider:
- Could a computer system be built to follow this algorithm easily?
- Are there algorithms you perform daily that would be very difficult for a computer?
- Is the algorithm you use the fastest one? Are there real-world limitations that prevent you from doing it faster?
- If the algorithm you use the most efficient one (the least number of steps) or simply the one that you learned first?
- How do you share your “algorithms” with others so they can follow along?
Scratch Sorting Algorithms
- Download the starter file from KSOL
- Implement the Bubble Sort Algorithm
- Verify that the list is sorted
- Submit via K-State Online
Due Wednesday, 2/19 10:00 PM
Bubble Sort
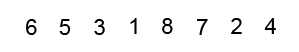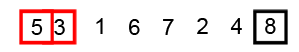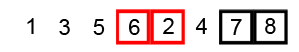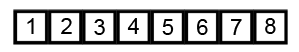
Image Source: Wikipedia
- Compare the first two elements
- If they are out order, swap them
- Move one element over and repeat
- When the end is reached, start over
- Repeat these steps as many times as the number of items in the list