CIS 115
Lecture 11: Cryptography
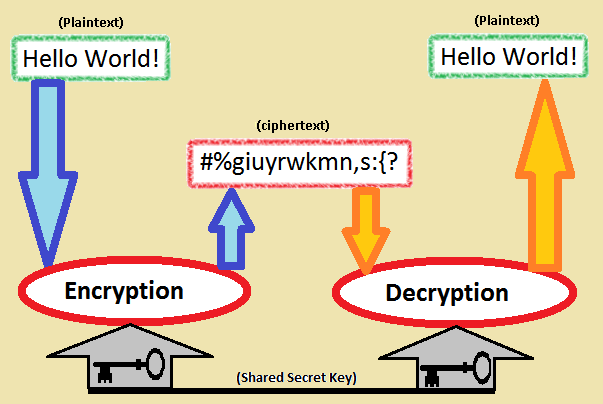
Cryptography
- Study of ways to communicate securely and privately in the presence of third parties
- Charles Babbage, Edgar Allan Poe, Alan Turing, and Claude Shannon were all involved in cryptography.
Message to the Class
TSTEPHAAXLISLAESCEMQIYQMessage to the Class
TSTEPHAAXLISLAESCEMQIYQT H I S I S A S C Y T A L E Q E X A M P L E QEarly Ciphers
- Substitution Ciphers
- Cryptoquip - Easily Breakable
- Polyalphabetic Ciphers
- First described by Al-Kindi in the 9th century
- Later explained by Leon Battista Alberti in 1467
Image Source: Wikipedia

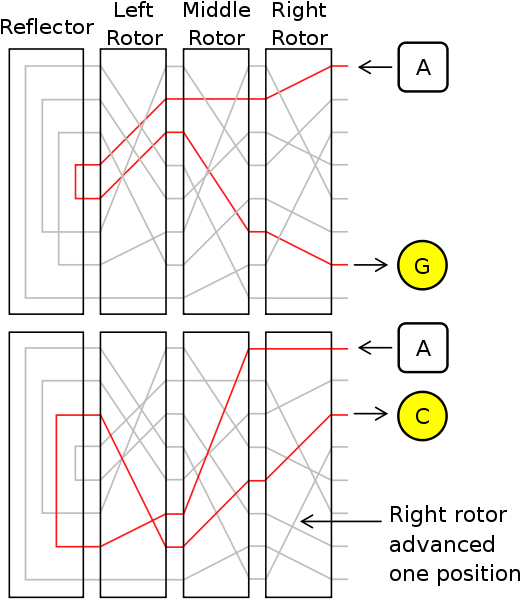
Image Source: Wikipedia
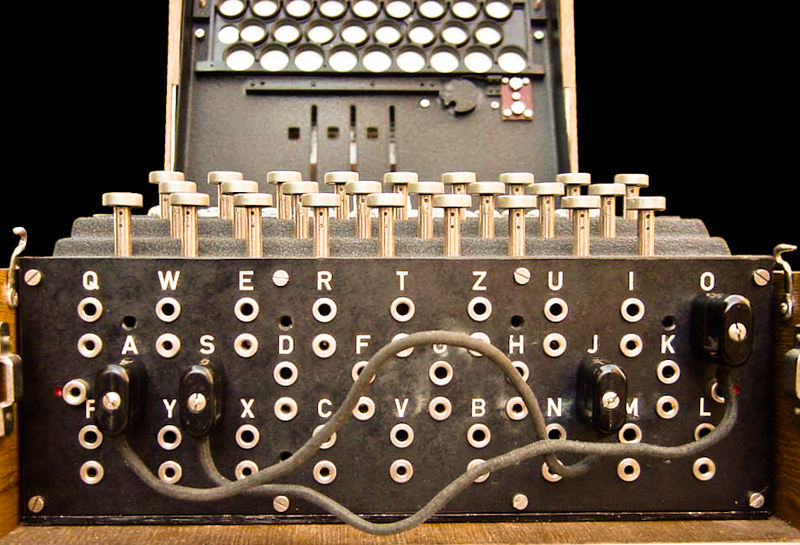
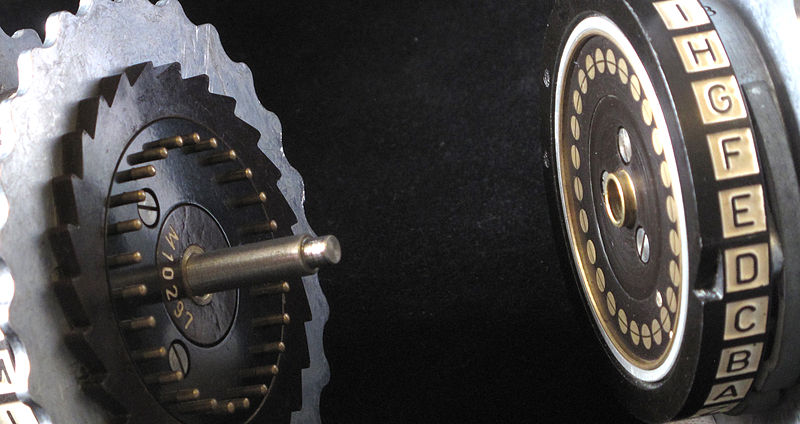
Enigma Key
- Choice and order of rotors
- Initial position of rotors
- Ring setting on rotors
- Plug connections
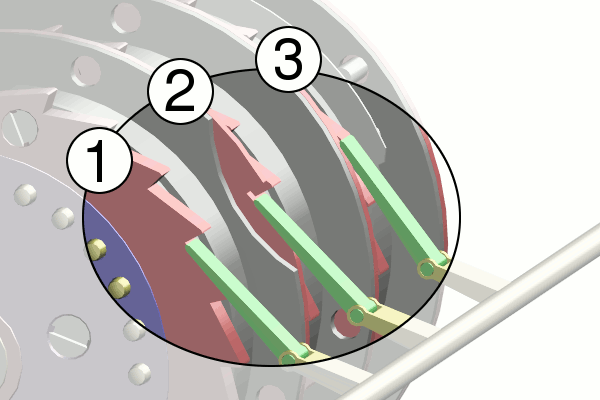
Enigma Operation
- Set wheels to today's key from codebook
- Operator chooses message key
- Encode message key TWICE to avoid errors
- Set wheels to message key
- Encrypt and send message
Enigma Stengths
- Many factors to the encryption
- Had up to 8 different wheels to choose from by the end of the war
- 150 Trillion different setups
Enigma Weaknesses
- A letter would never encrypt to itself
- Plugboards were reciprocal
- Wheels were not similar enough (could determine which wheels were used)
- Poor policies and procedures
Cracking Enigma
- 1932 - First cracked by Marian Rejewski of Poland
- 1938 - Germany added 2 wheels
- 1939 - Alan Turing creates Bombe
- 1945 - Almost every message deciphered within 2 days
Impact
“My own conclusion is that it shortened the war by not less than two years and probably by four years … we wouldn't in fact have been able to do the Normandy Landings, even if we had left the Mediterranean aside, until at the earliest 1946, probably a bit later.”
-Sir Harry Hinsley
British Intelligence Historian
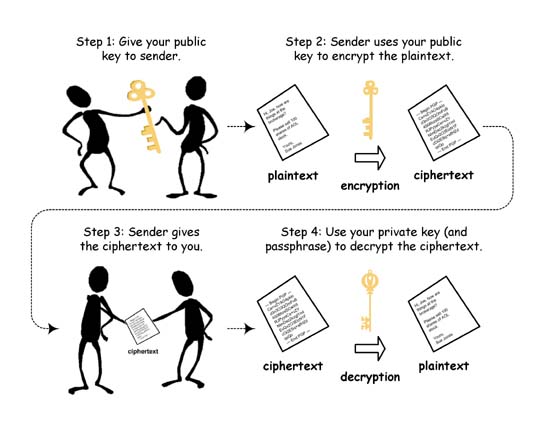
RSA Encryption
- Developed in 1977
- Named for the 3 creators (Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, Lenonard Adleman)
- Uses the product of 2 large prime numbers to generate a key
- Key strength depends on the difficulty of factoring large numbers
RSA Example
- Choose 2 distinct prime numbers
p and q - Compute their product n = pq
- Compute the totient t of n:
t = (p - 1)(q - 1)
RSA Example
- Choose any number e less than t that is coprime to t (they share no common factors but 1)
- Calculate d as the modular multiplicative inverse of e (mod t)
e * x = 1 (mod t)
RSA Keys
- Public Key : (n, e)
- Encode: c = me (mod n)
- Private Key : (n, d)
- Decode: m = cd (mod n)
Assignments
- Read and be prepared to discuss:
- Tubes Chapter 1: The Map & Chapter 2: A Network of Networks
- Blog 5: Making Meaning: POTS - Due 3/3 10:00 PM
- Scratch Stoplight Project - Due 2/28 10:00 PM
- Scratch HPC Sum Project - Due 3/5 10:00 PM
Blog 5: Making Meaning - POTS
Now that we’ve finished reading the first textbook, it is time to step back and think about what we read. Write about your reactions to it and what you learned from it. I’d recommend almost treating this like an in-depth book review for others who are interested in reading the book, but don’t mind some spoilers. Some questions I’d like you to answer:
- How did you feel reading this book? Engaged? Bored? Interested?
- What was the most interesting thing you learned?
- Were there any parts of the book you didn’t like?
- Were there any terms or concepts that you looked up (Googled) to find more information about? What were they? What did you find?
- Did this book help explain things you didn’t know about computers?
- Would you recommend this book to a friend that wanted to know more about computers?
RSA Activity
- Fill out the RSA Activity Worksheet