CIS 115
The History
of the Internet
J.C.R Licklider
"A network of such [computers], connected to one another by wide-band communication lines [which provided] the functions of present-day libraries together with anticipated advances in information storage and retrieval and [other] symbiotic functions."
J.C.R. Licklider - 1960
Man-Computer Symbiosis
Intergalactic Computer Network
- Global network of computers
- Instantly access data and programs from any other computers
Image Source: Wikipedia
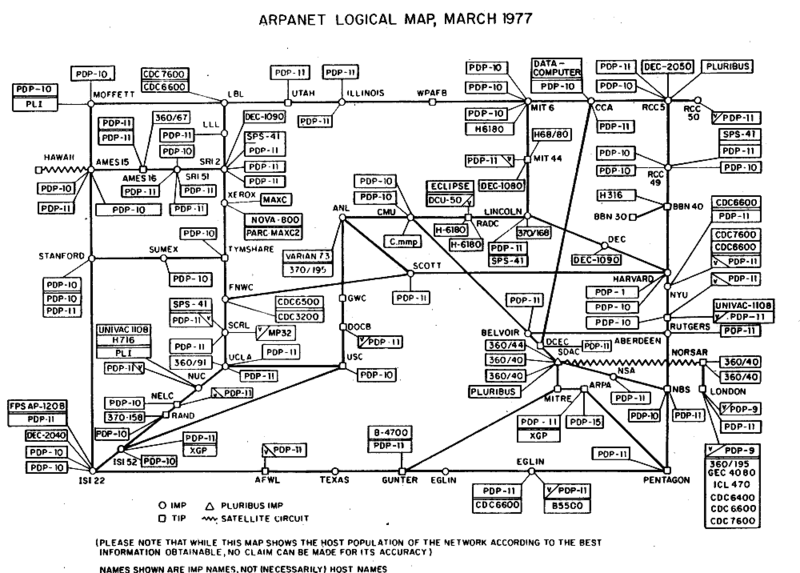
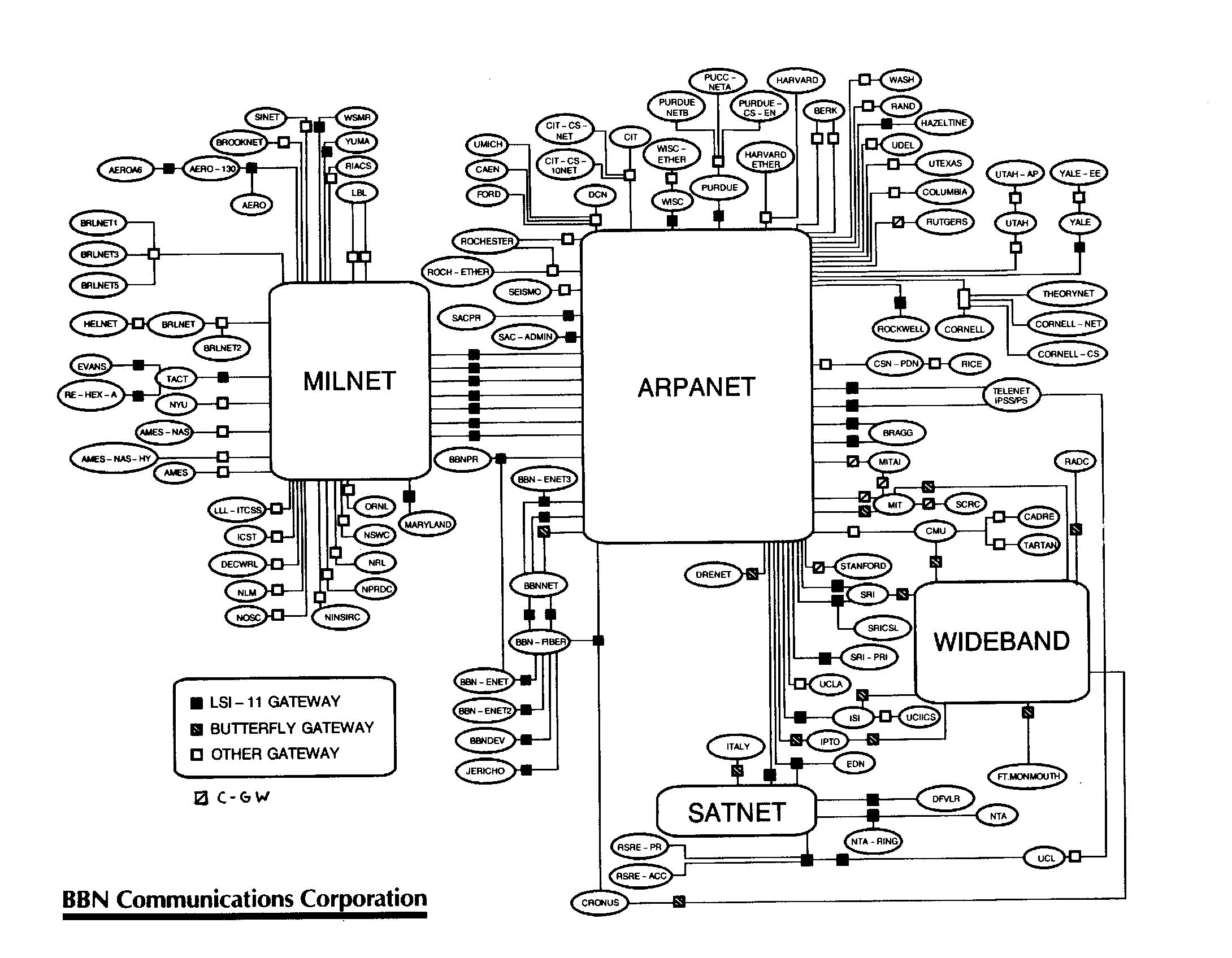
Lots of Networks
- ARPANET
- NPL
- Merit
- CYCLADES
- X.25 & Public Networks
- UUCP - Usenet
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- Small networks could talk via a common standard (or protocol)
- No single point of failure in a system
- Computers could acknowledge successful transmission or request a retransmittal of missing data
- Data transmission was tolerant of errors and lost data
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Method for requesting a World Wide Web resource (web page) from a web server using the Internet
- Commonly runs on top of TCP
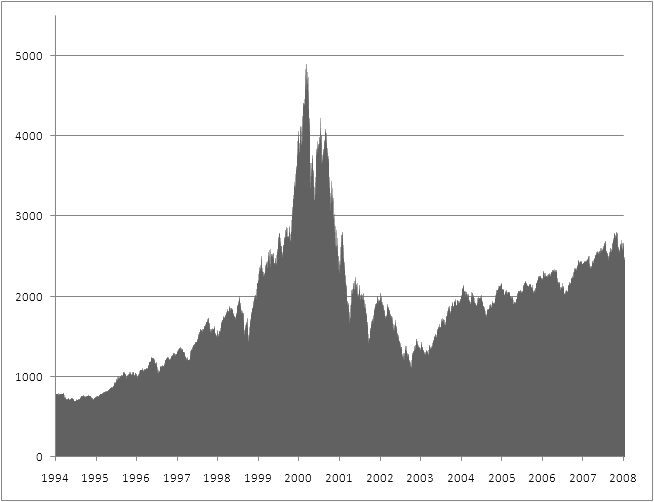
- Infospace: $1,305/share in March 2000; $2.67 by June 2002
- The Learning Company: Bought for $3.5 billion in 1999; sold for $27.3 million in 2000
- Geocities: Purchased by Yahoo for $3.57 billion in 1999, closed 10 years later
The Internet Today
- Web 2.0 and Social Media
- Ubiquitous Internet Access
- Mobile Devices
- Rise of Search Engines
Assignments
- Read and be prepared to discuss:
- Tubes Chapter 1 - The Map
- Blog 3: Making Meaning: POTS - Due 10/3 10:00 PM
- Scratch FSM Project - Due 9/27 10:00 PM
Blog 3: Making Meaning: POTS
Now that we’ve finished reading the first textbook, it is time to step back and think about what we read. Write about your reactions to it and what you learned from it. I’d recommend almost treating this like an in-depth book review for others who are interested in reading the book, but don’t mind some spoilers. Some questions I’d like you to answer:
- How did you feel reading this book? Engaged? Bored? Interested?
- What was the most interesting thing you learned?
- Were there any parts of the book you didn’t like?
- Were there any terms or concepts that you looked up (Googled) to find more information about? What were they? What did you find?
- Did this book help explain things you didn’t know about computers?
- Did this book leave you with any questions unanswered?
- Would you recommend this book to a friend that wanted to know more about computers?
Work on Topic Research