CIS 115
Bits and Boolean Algebra
Aristotelian Logic
- Premise:
All men are mortal
Socrates is a man - Conclusion:
Therefore, Socrates is mortal
Boolean Logic
- Premise:
A ∧ B
B ∧ C - Conclusion:
A ∧ C
Note: This translation is somewhat flawed, but I'll leave that to a later course in logic or philosophy to describe why.
Boolean Symbols
∧ &&
∨ ||
⊕
¬ !
And
Or
Exclusive Or (XOR)
Not
Truth
- Premise:
A ∧ B → TRUE
B ∧ C → TRUE - Conclusion:
A ∧ C → TRUE
Truth
- Premise:
A ∧ B → TRUE
B ∧ C → FALSE - Conclusion:
A ∧ C → FALSE
De Morgan's Law
Negation (inverse) of a logic statement
¬ ( A ∧ B ) = ( ¬ A ) ∨ ( ¬ B)
¬ ( A ∨ B ) = ( ¬ A ) ∧ ( ¬ B)
Distribute the negative (¬) then swap ands (∧) and ors (∨)
Boolean Algebra
- ∨ works like addition ( + )
- ¬ works like negation ( − )
- ∧ works like multiplication ( × )
- Associative: (A ∧ B) ∧ C = A ∧ (B ∧ C)
- Commutative: (A ∧ B) = (B ∧ A)
- Distributive:
A ∧ (B ∨ C) = (A ∧ B) ∨ (A ∧ C)
A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits

Image Source: MIT
"...possibly the most important, and also the most famous, master's thesis of the century."
- Psychologist Howard Gardner (via Wikipedia)
Logic Gates
AND 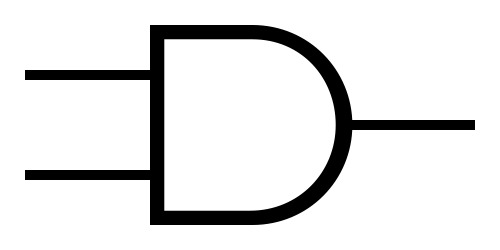 |
OR 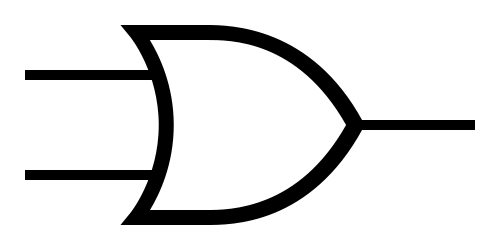 |
XOR 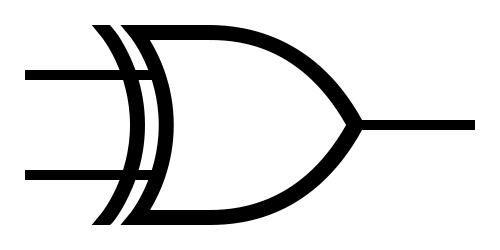 |
NOT 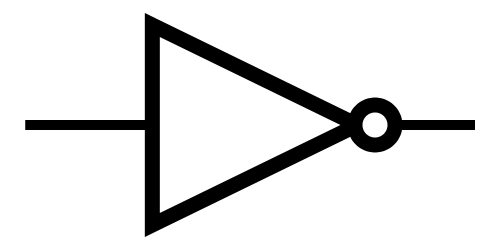 |
NAND 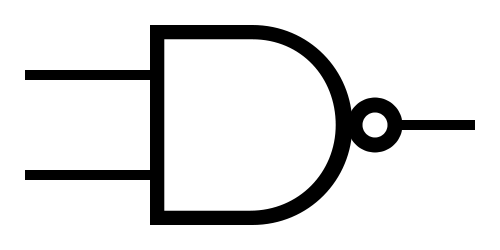 |
NOR 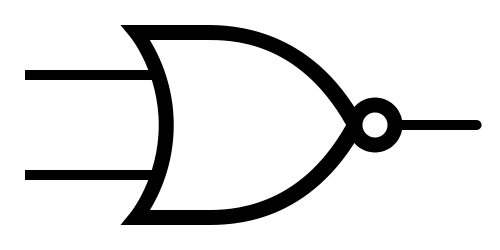 |
XNOR 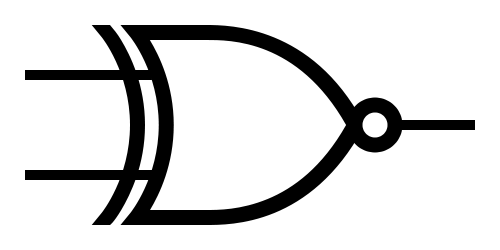 |
Note: The little circle at the end of the NOT gate is the only part that matters.
Boolean Values
Boolean |
Binary |
Electrical |
|---|---|---|
TRUE |
1 |
ON |
FALSE |
0 |
OFF |
Note: These values are traditionally used in theory. In many electronic systems and programming languages these values may be reversed for various reasons. Check the manual!
Example 1
A |
B |
C |
OUT |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
(A ∧ C) ∨ (B ∧ C)
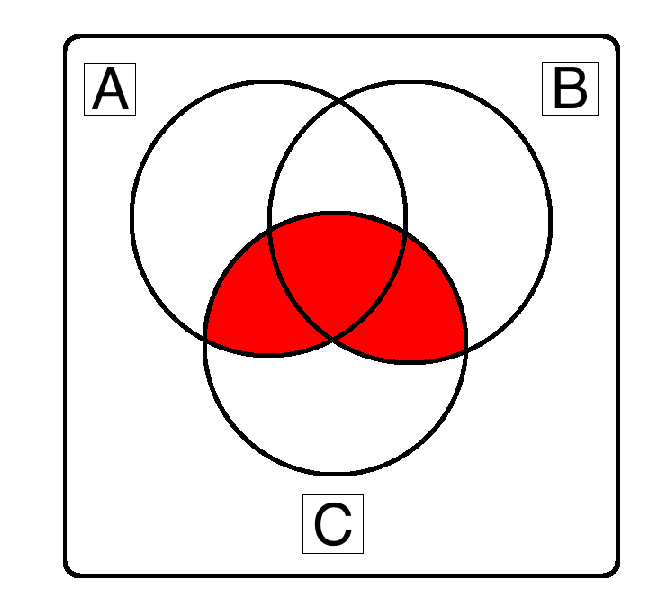
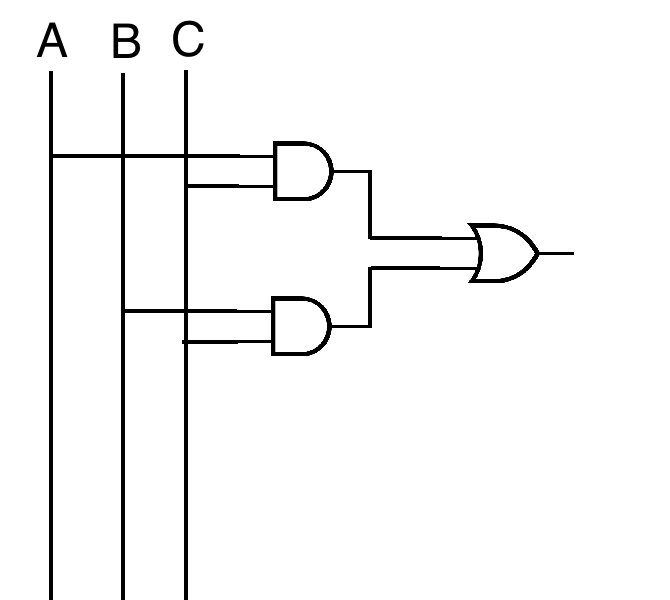
C ∧ (A ∨ B) works as well
Example 2
A |
B |
C |
OUT |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
¬A ∧ ( B ∨ C )
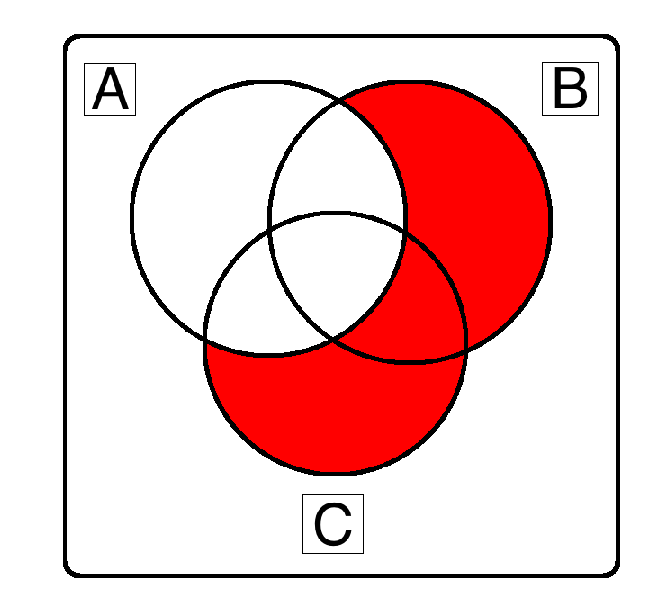
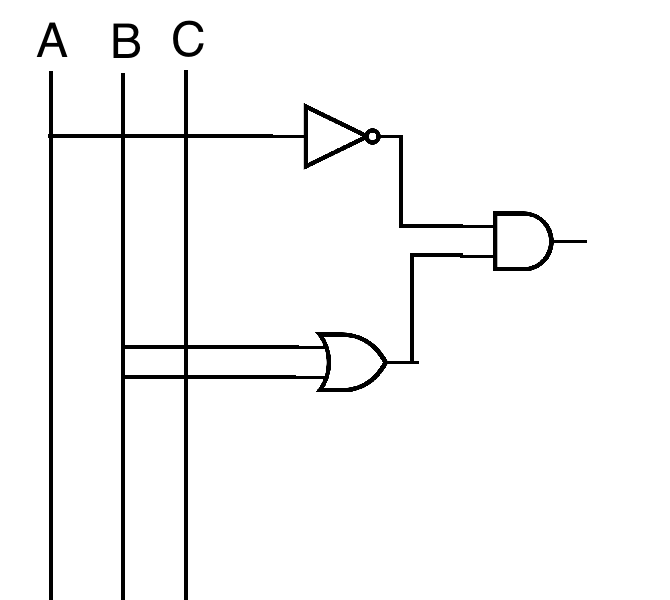
( ¬A ∧ B) ∨ ( ¬A ∧ C) works as well
Example 3
A |
B |
C |
OUT |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
( A ⊕ B ) ∧ C
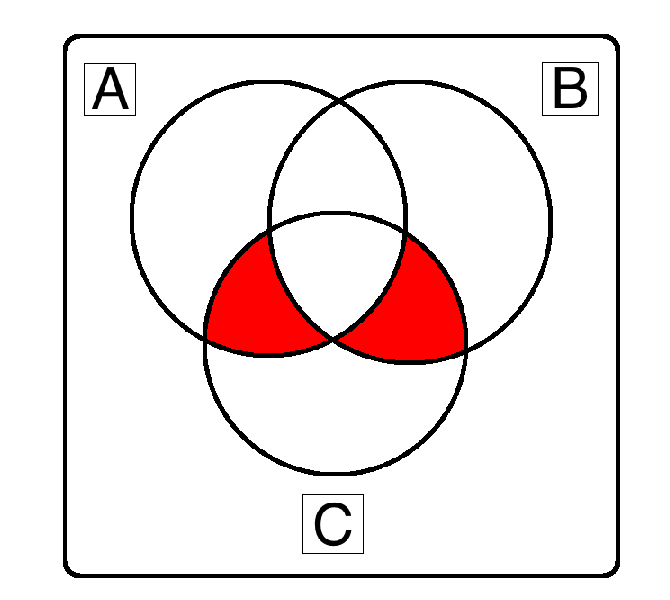
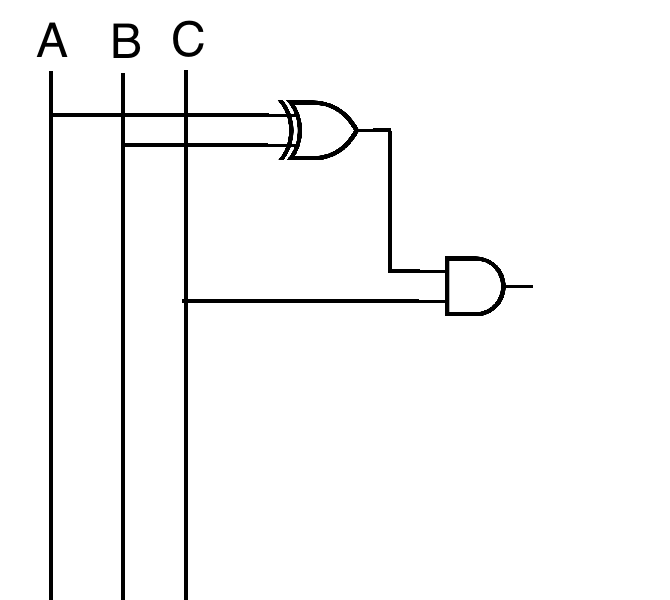
(A ∧ C) ⊕ (B ∧ C) works
(A ∧ ¬B ∧ C) ∨ (¬A ∧ B ∧ C) works
Example 4
A |
B |
C |
OUT |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
¬ ( A ∧ B ∧ ¬C )
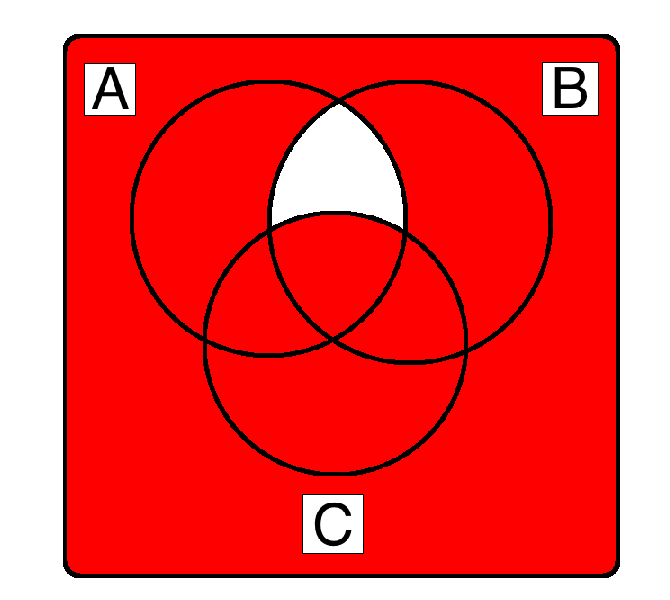
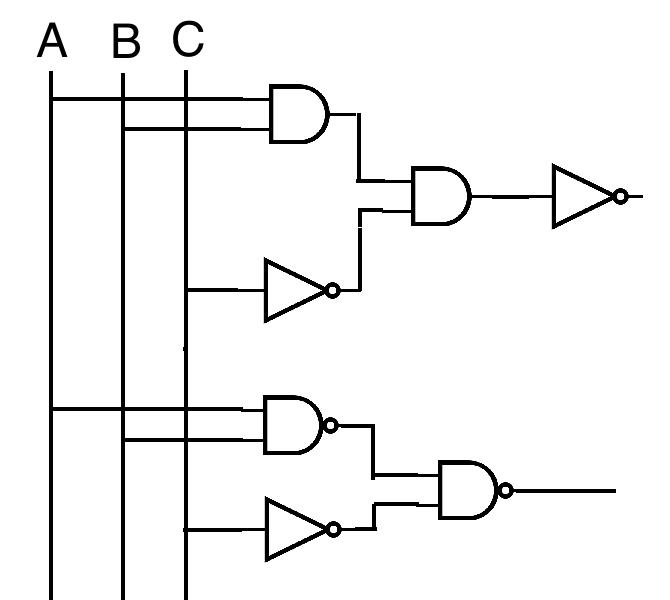
By De Morgan's Law
( ¬A ∨ ¬B ∨ C ) works as well
Next Steps
- Programming
- Finite State Machines
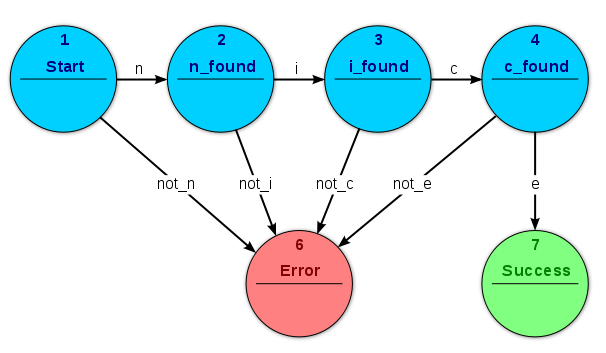
Image Source: Wikipedia
Assignments
- Read and be prepared to discuss:
- Pattern on the Stone
Chapter 3: Programming
- Pattern on the Stone
- Blog 1: Personal Biography - Due Tuesday 9/8 10PM
- Scratch Project 1 - Due 9/15 10PM
Blog 1: Personal Biography
Tell us a little about yourself. This is your chance to let us know who you are and what interests you. Some questions you can answer to get you started are below, but feel free to be as creative and expressive as possible introducing yourself.
- Where are you from?
- Why did you choose to come to Kansas State?
- What interests you about Computing Science?
- Do you have any hobbies?
- What is your family like?
- Have you had any interesting jobs or experiences?
- What do you want to do after you graduate?
Scratch Project (Part 1)
- Download the starter file from KSOL
- Follow the instructions to complete the project
Due: Sept. 15th, 10:00 PM
Booleans in Scratch
And  |
Or  |
Not  |
Getting Boolean Values
Less Than  |
Greater Than  |
Equals  |
Mouse Down  |
Key Pressed  |
Using Boolean Values
If block  |
If Else block |
Scratch Variables
Variable  |
Set Variable 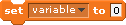 |
Change Variable  |
Show Variable  |
Hide Variable 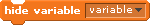 |